- Egypt Tour Magic
- Egypt Tour Packages
- Excursions in Egypt
- Cairo Tours and Excursions
- Hurghada Tours and Excursions
- Soma Bay Tours and Excursions
- Makadi Bay Tours and Excursions
- Sahl Hasheesh Tours and Excursions
- El Gouna Tours and Excursions
- Marsa Alam Tours and Excursions
- Port Ghalib Tours and Excursions
- El Quseir Tours and Excursions
- Dendera and Abydos Day Tours
- Aswan Tours and Excursions
- Luxor Tours and Excursions
- Alexandria Tours and Excursions
- Sharm El Sheikh Tours and Excursions
- Top Rated Tours in 2025
- Optional Excursions in Egypt
- Private Transfer
- Blogs About egypt
- Ancient Egypt
- What You Need To know Before Your First Trip To Egypt
- Best Places to Visit in Egypt 2025
- Top Attractions in Red Sea Resorts 2025
- Top 10 Tourist Activities in Egypt
- Top 30 Activities You Can’t Miss in Egypt
- The Guide to Guided Tours in Egypt
- Egypt’s Ancient and Modern History
- The Nile River
- The Deserts of Egypt
- Historical Sites in Egypt
- Cairo
- Alexandria
- Luxor
- Aswan
- The Red Sea
- Dendera Temple
- El Fayoum Oasis
- Bahariya Oasis
- Siwa Oasis
- Al Alamein
- Marsa Matruh
- Ancient Egyptian gods
- famous Egyptian dishes
- UNESCO World Heritage sites
- About Us
- Why Egypt Tour Magic
- Egypt Tour Magic
- Egypt Tour Packages
- Excursions in Egypt
- Cairo Tours and Excursions
- Hurghada Tours and Excursions
- Soma Bay Tours and Excursions
- Makadi Bay Tours and Excursions
- Sahl Hasheesh Tours and Excursions
- El Gouna Tours and Excursions
- Marsa Alam Tours and Excursions
- Port Ghalib Tours and Excursions
- El Quseir Tours and Excursions
- Dendera and Abydos Day Tours
- Aswan Tours and Excursions
- Luxor Tours and Excursions
- Alexandria Tours and Excursions
- Sharm El Sheikh Tours and Excursions
- Top Rated Tours in 2025
- Optional Excursions in Egypt
- Private Transfer
- Blogs About egypt
- Ancient Egypt
- What You Need To know Before Your First Trip To Egypt
- Best Places to Visit in Egypt 2025
- Top Attractions in Red Sea Resorts 2025
- Top 10 Tourist Activities in Egypt
- Top 30 Activities You Can’t Miss in Egypt
- The Guide to Guided Tours in Egypt
- Egypt’s Ancient and Modern History
- The Nile River
- The Deserts of Egypt
- Historical Sites in Egypt
- Cairo
- Alexandria
- Luxor
- Aswan
- The Red Sea
- Dendera Temple
- El Fayoum Oasis
- Bahariya Oasis
- Siwa Oasis
- Al Alamein
- Marsa Matruh
- Ancient Egyptian gods
- famous Egyptian dishes
- UNESCO World Heritage sites
- About Us
- Why Egypt Tour Magic
Ancient Egypt: Mysteries, Monuments, and Legends
Ancient Egyptian civilization, one of the oldest and most influential cultures in world history, thrived for over 3,000 years along the fertile banks of the Nile River. Renowned for its monumental architecture, the Egyptians constructed iconic structures such as the pyramids, the Great Sphinx, and grand temples. Their advanced engineering and mathematical knowledge enabled them to achieve remarkable feats. The Egyptian writing system, known as hieroglyphics, played a crucial role in recording history, religion, and administration. Papyrus, the material they invented for writing, allowed for the preservation of literature and scientific knowledge. In the field of medicine, Egyptians made significant advancements in surgery, herbal remedies, and anatomy, laying the groundwork for modern medical practices. Religion and the belief in an afterlife were central to Egyptian life, with mummification and elaborate burial practices to ensure safe passage to the next world. Their mastery in astronomy, creating a calendar based on lunar and solar cycles, and their agriculture, supported by advanced irrigation techniques, contributed to their prosperity. The influence of Ancient Egypt on art, science, mathematics, and philosophy continues to resonate today, shaping various fields and inspiring awe worldwide.
1. Food in ancient Egypt
Food in ancient Egypt reflected the diversity of daily life for the ancient Egyptians, and relied heavily on local resources available in the Egyptian environment, such as grains that were cultivated along the banks of the Nile River, vegetables grown in fertile lands near the river, and fruits provided by fruit-bearing trees in various regions. Additionally,
2. Ancient Egyptian Myths
The creation myth in Ancient Egypt varies significantly across regions, but all versions agree that the universe originated from chaos or the “primordial waters” (Nun). In the Heliopolitan version, the myth revolves around the god Ra, who emerged from Nun and created the earth, the sun, and other gods. Ra’s creation marked the beginning of cosmic order and the establishment
3. The Seven Wonders of the Ancient World
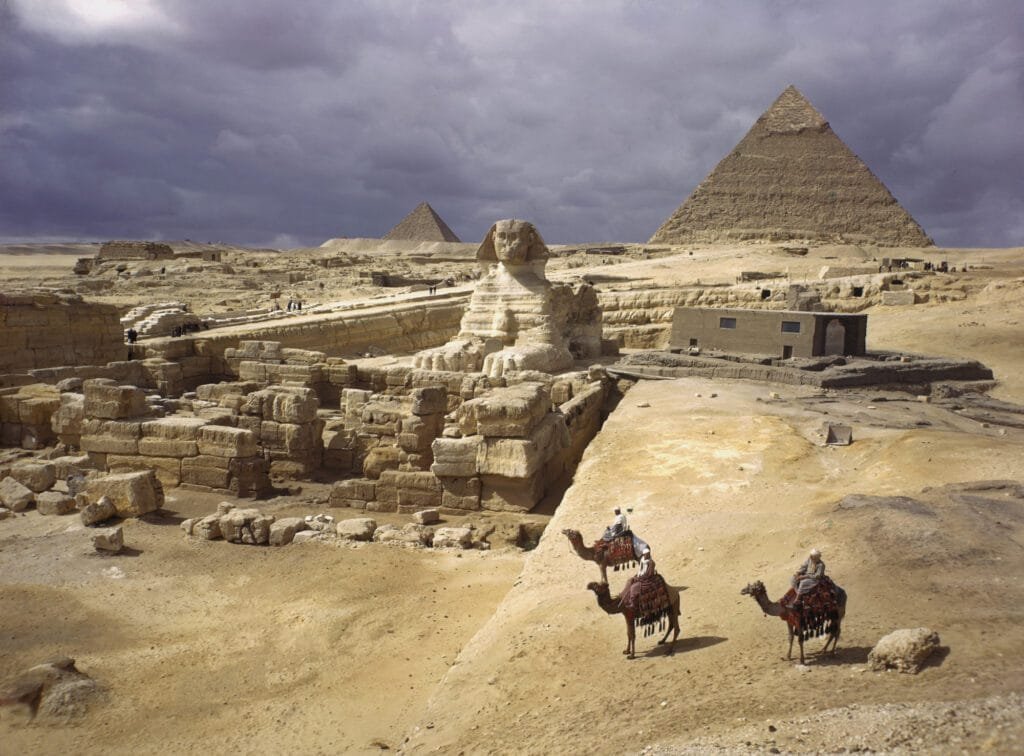
The Great Pyramid of Giza, also known as the Khufu Pyramid, is the most iconic and largest pyramid of the Giza Pyramid Complex in Egypt. As one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, it holds immense cultural, historical, and architectural significance, continuing to awe visitors from around the globe.
4. Marriage in Ancient Egypt
Marriage in Ancient Egypt was viewed not just as a social contract between individuals but as a divine institution. The ancient Egyptians believed that marriage was a reflection of the cosmic order, and it played a crucial role in ensuring the stability and balance of the world. This belief was rooted in the mythology surrounding the gods,
5. Ancient Egyptian Languages
The ancient Egyptian languages represent one of the oldest and most significant language families in human history. These languages, over thousands of years, evolved to serve the administrative, religious, and cultural needs of a vast and complex civilization. The development of the Egyptian language was intrinsically linked to the kingdom’s political structure
6. Ancient Egyptian Civilization
The Ancient Egyptian Civilization is one of the oldest and most remarkable civilizations in human history, emerging along the banks of the Nile River, which provided the vital resources and fertile lands that sustained this civilization for over three millennia. This great civilization began around 3100 BCE with the unification of Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt by King Narmer (also known as Menes),
7. Education in Ancient Egypt
Education in Ancient Egypt was a highly structured and integral part of the society, deeply connected to the administration, religion, and intellectual life of the civilization. It primarily served the elite classes, with a strong focus on preparing individuals for roles in government, religion, and specialized professions. Education took place in temples,
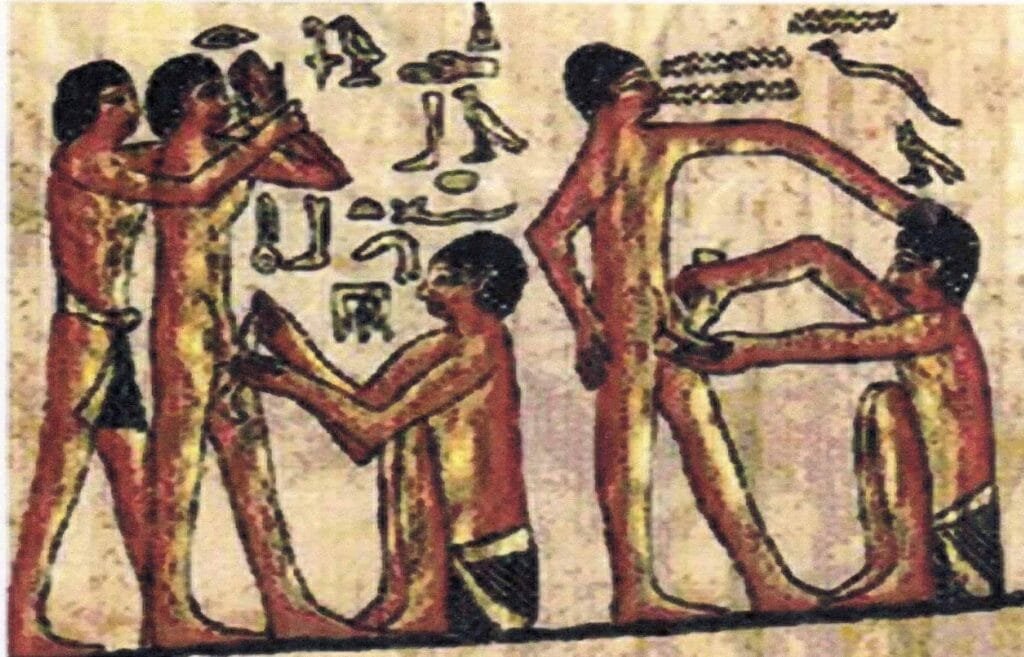
8. Ancient Egyptian medicine
Ancient Egyptian medicine was one of the most advanced and influential medical systems in the ancient world. It combined practical medical knowledge with spiritual and religious beliefs, demonstrating a sophisticated understanding of anatomy, diseases, and healing. The Egyptians believed that illness resulted from both physical and spiritual causes,
9. Key Events in Ancient Egyptian History
Around 3100 BCE, King Narmer (also known as Menes) successfully united Upper Egypt (southern Egypt) and Lower Egypt (northern Egypt), marking the foundation of a unified Egyptian state. This unification is considered one of the most significant events in ancient Egyptian history,
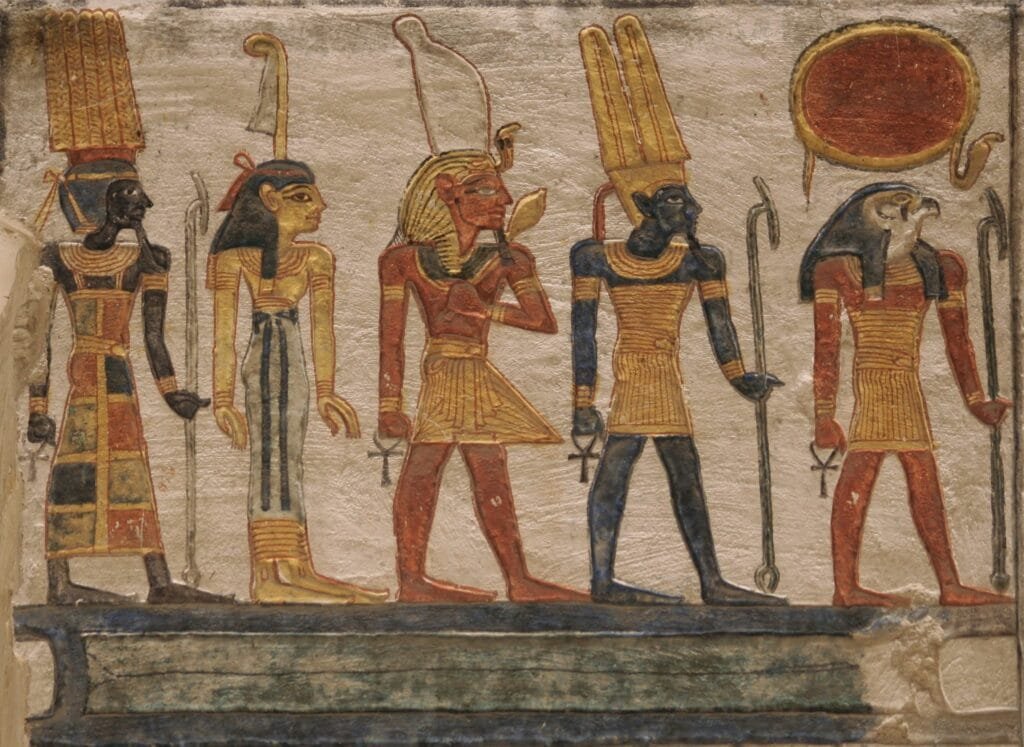
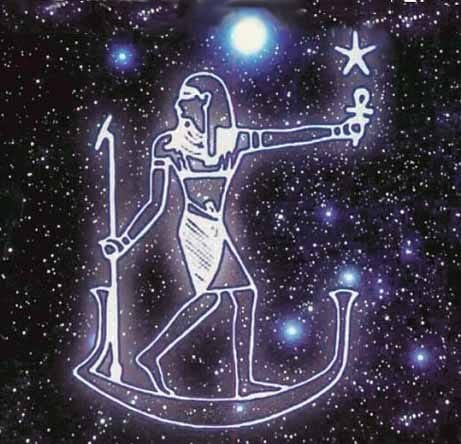
10. Ancient Egyptian gods
The ancient Egyptian gods were central to the religion, culture, and daily life of one of history's most enduring civilizations. These deities, numbering in the hundreds, each represented different aspects of the natural world, human experience, and cosmic order. From Ra,
11. Ancient Egypt’s Kings
pharaohs of ancient Egypt were more than mere rulers; they were considered divine intermediaries between the gods and their people, embodying the nation's spiritual and political authority. These kings, from the legendary Khufu, the builder of the Great Pyramid,
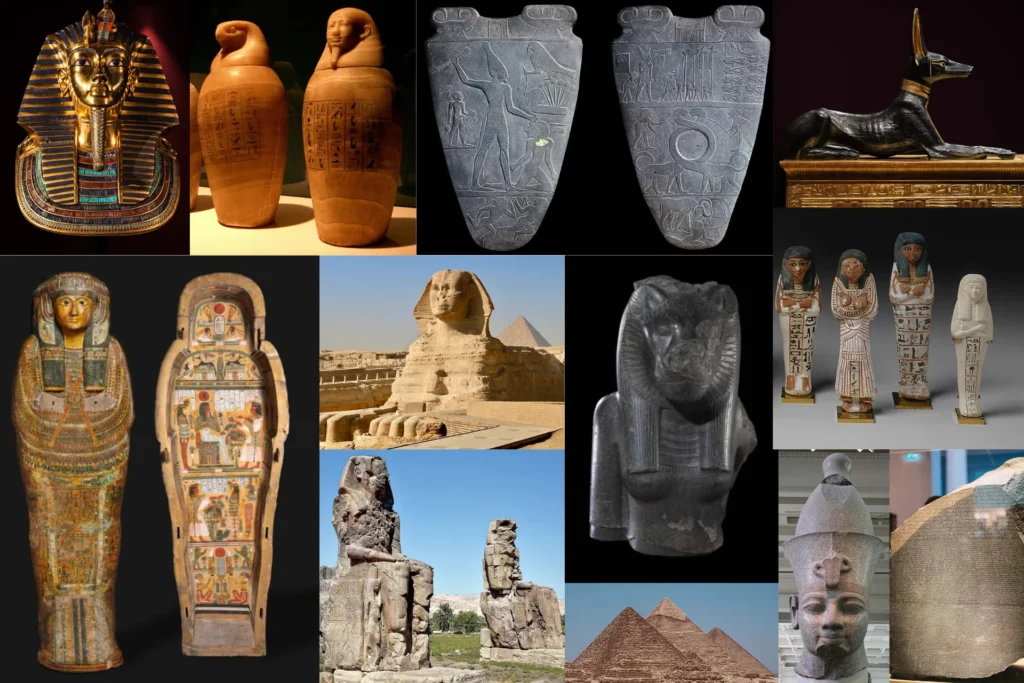
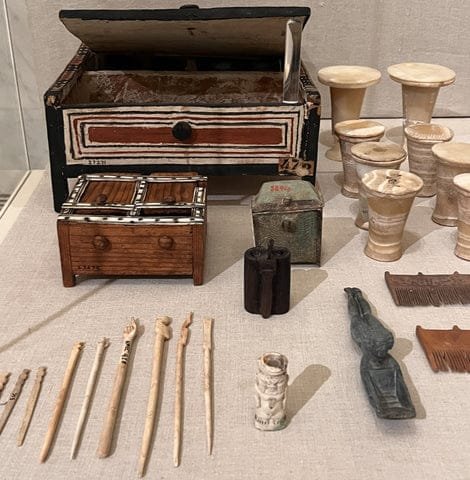
12. Acient Egyptian artifacts
This collection showcases some of the most celebrated and historically significant artifacts from Ancient Egypt. These treasures not only highlight the incredible craftsmanship of Egyptian artisans but also provide valuable insights into the culture, religious beliefs,
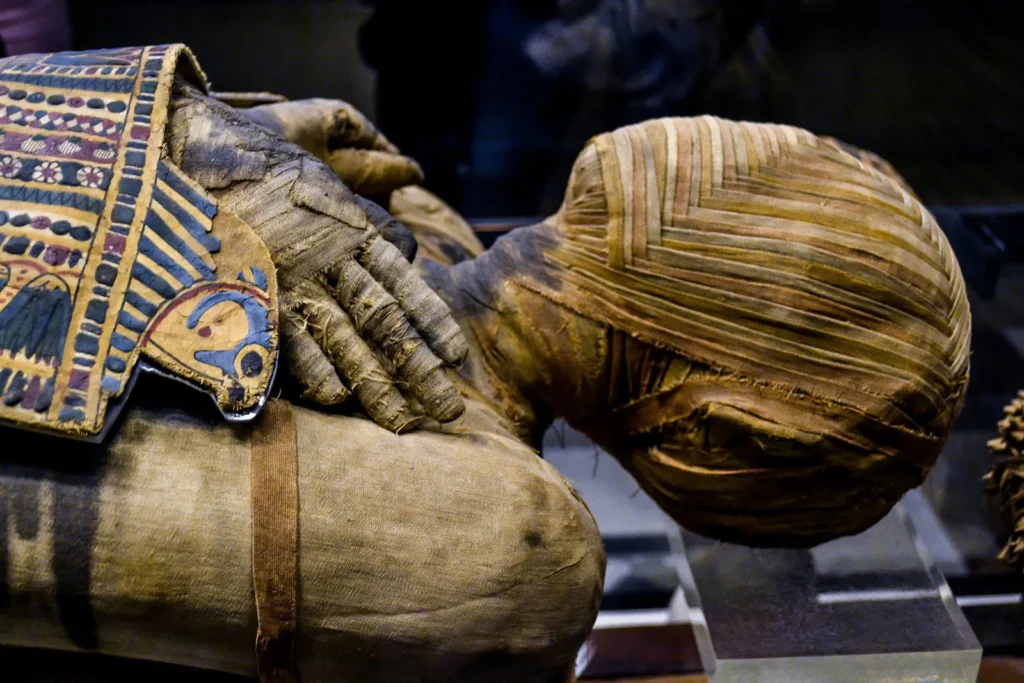
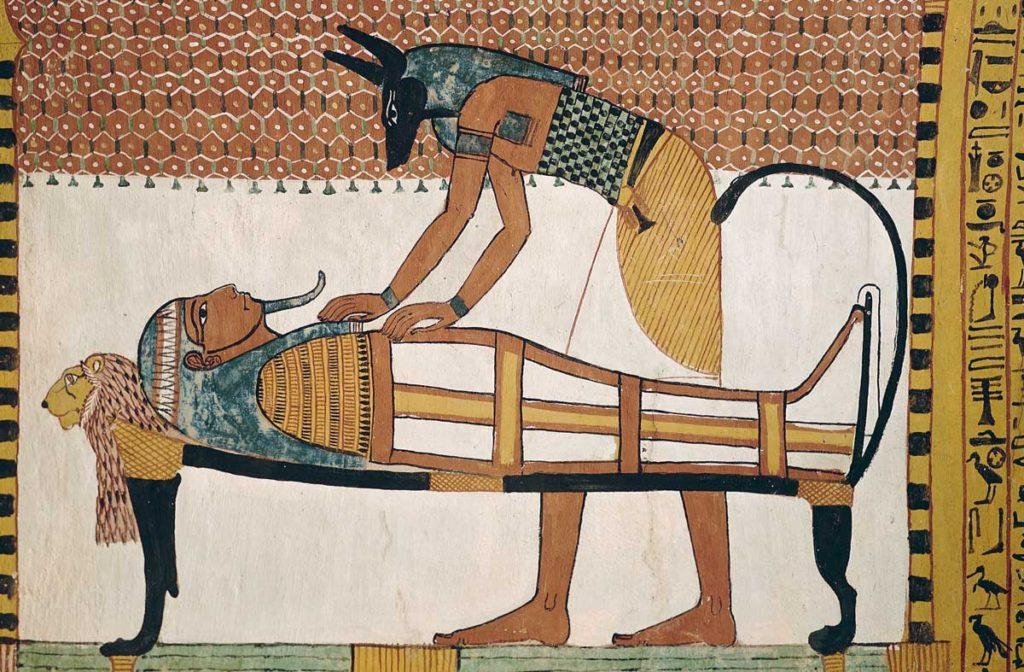
13. The Mummies of Ancient Egypt
mummies of ancient Egypt are not just extraordinary for their remarkable preservation, but they also provide a window into the intricate and captivating world of one of history’s most advanced civilizations. These mummies, from powerful pharaohs like Ramses II and Khufu to influential queens
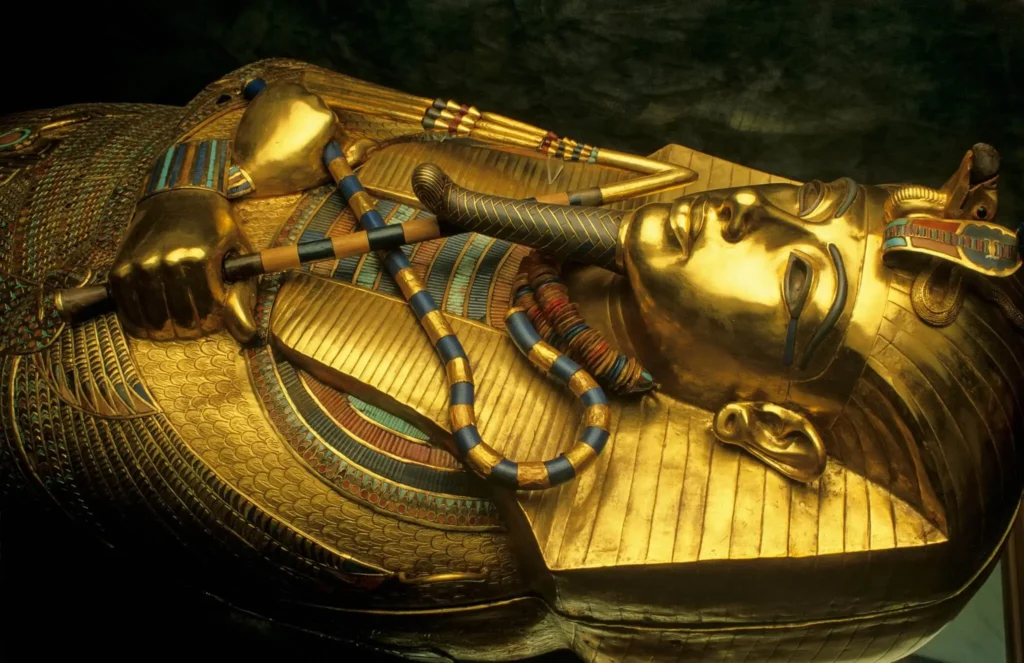
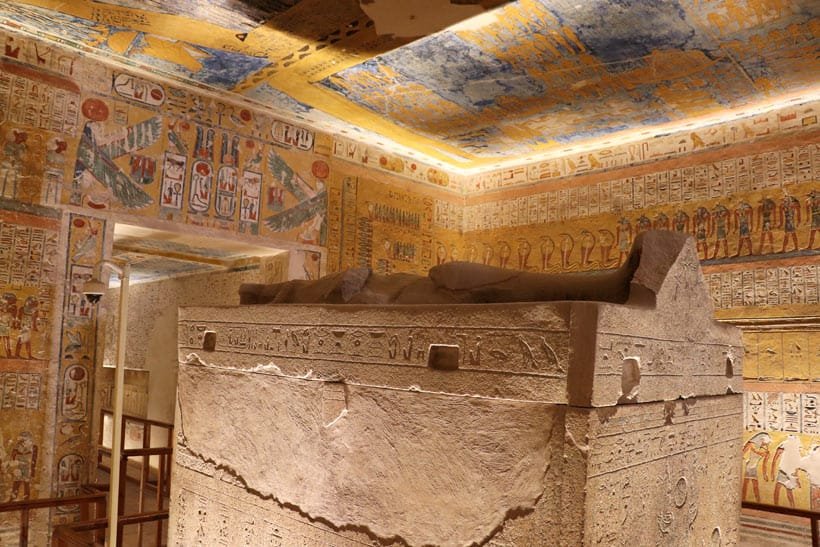
14. The Most Famous Sarcophagi of Ancient Egypt
These sarcophagi are among the most famous and significant archaeological finds in Egypt. Each one provides a unique glimpse into the lives of the Pharaohs, their religious beliefs, and the artistic mastery of ancient Egyptian craftsmanship. The detailed carvings, materials,
15. The Role of Queens in Egyptian Rule
Ancient Egypt, one of the oldest and most fascinating civilizations in history, was home to remarkable achievements in various fields such as art, architecture, science, and religion. However, what often goes unnoticed is the significant role women played in Egypt’s leadership and governance. Throughout Egypt’s long
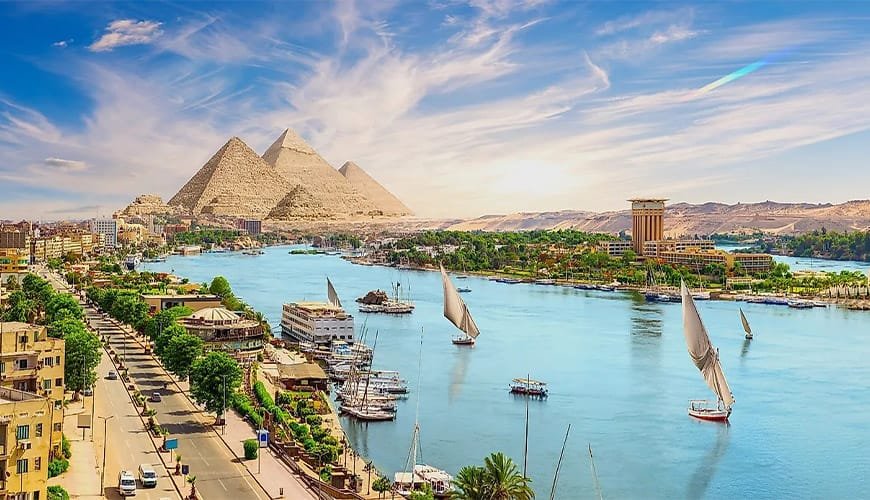
16. The Nile River The Lifeblood of Ancient Egypt
The Nile River, one of the longest and most important rivers in the world, played a central role in the development of ancient Egyptian civilization. Far more than just a river, the Nile was the lifeblood of Egypt, supporting the country’s agriculture, economy,
17. Life Expectancy in Ancient Egypt
Life expectancy in Ancient Egypt varied widely due to a combination of factors such as disease, social status, nutrition, and environmental conditions. Ancient Egyptians are often remembered for their great accomplishments in architecture, medicine, and culture, but their daily lives were shaped by the harsh realities of life expectancy. Let’s take a closer look at how long people lived, the challenges they faced, and what contributed to their survival or early demise.
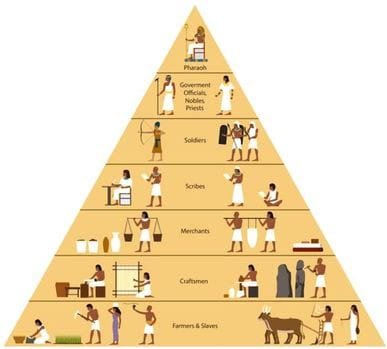
18. Jobs in Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt is one of the most fascinating civilizations in history, renowned for its incredible achievements in art, architecture, medicine, and social organization. At the heart of these achievements were the hardworking individuals who performed a vast array of jobs that helped sustain the society for thousands of years. From monumental pyramid builders to skilled scribes, Ancient Egypt’s labor force was diverse and essential for the civilization’s success.
19 . The Police in Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt, a civilization known for its monumental achievements and rich culture, also had a well-developed system of law and order. Much like the modern police forces of today, the ancient Egyptian police played a crucial role in maintaining stability and ensuring that the laws set forth by the pharaohs were followed. These early law enforcers were involved in various aspects of society,
20 . Ancient Egyptian Gardens
When we think of Ancient Egypt, we often imagine majestic pyramids, intricate hieroglyphs, and powerful pharaohs. But nestled in the heart of this ancient civilization were places of tranquility and beauty: the gardens. These gardens were not only designed to enhance the landscape but were deeply intertwined with Egypt’s spiritual and cultural life. From royal palaces to temple courtyards,
21 . Ancient Egypt History
Ancient Egypt, one of the world’s earliest and most influential civilizations, spanned over 3,000 years and profoundly shaped the course of human history. Situated along the fertile banks of the Nile River, Egypt’s strategic location allowed it to develop a unique culture that fused innovation, religion, art, and governance. From the construction of the awe-inspiring pyramids to ...
22 . Ancient Egypt religion
Religion played a central role in the life of Ancient Egypt, influencing nearly every aspect of Egyptian culture, including politics, art, daily life, and death. The Egyptians practiced a polytheistic religion, meaning they believed in and worshiped a vast number of gods and goddesses, each of whom had specific roles, attributes, and responsibilities. The Egyptians believed that the gods ...
23 . Ancient egypt culture and traditions
Ancient Egyptian culture is one of the most fascinating and enduring cultures in human history. It lasted for over 3,000 years and influenced many other civilizations. The Egyptians were known for their rich traditions, beliefs, and remarkable achievements in various fields. Here’s an overview of some key aspects of their culture and traditions...
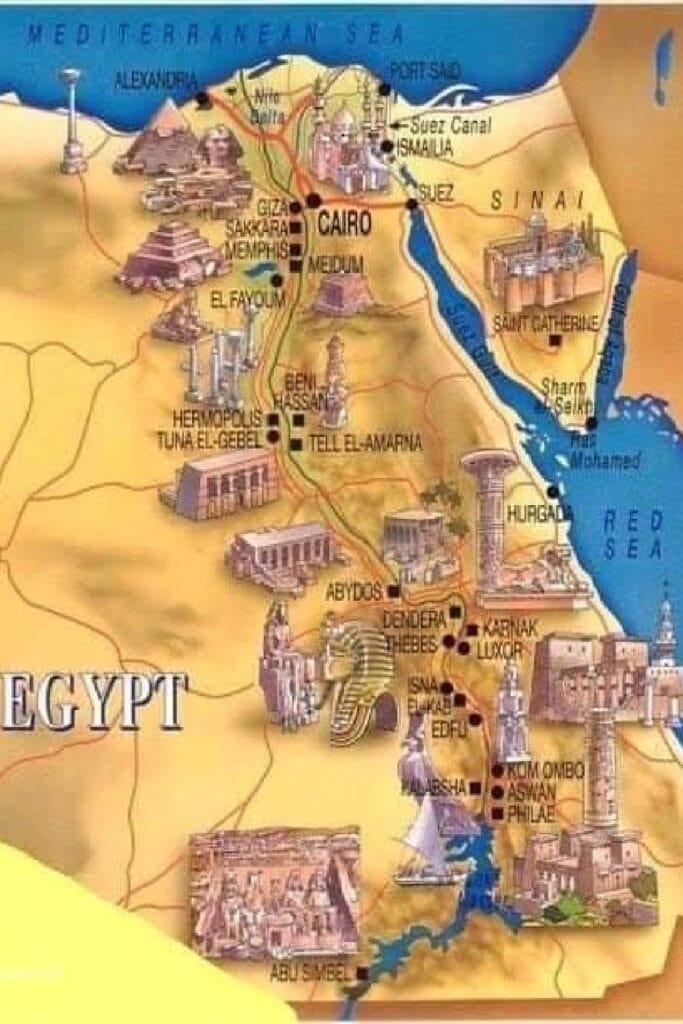
24 . The Ancient Egypt Map
Ancient Egypt, an awe-inspiring civilization that thrived for over 3,000 years, was defined by its unique geographical features. The map of Ancient Egypt is centered around the Nile River, which played a pivotal role in shaping the civilization. The landscape, divided into Upper and Lower Egypt, was a blend of fertile land, deserts, ...
25 . Science and Astronomy in Ancient Egypt
The ancient Egyptians were among the earliest civilizations to closely observe the skies, developing a profound understanding of astronomy that influenced almost every aspect of their lives. From religion and agriculture to architecture and art, the movements of the stars and planets were integral to the Egyptians’ worldview
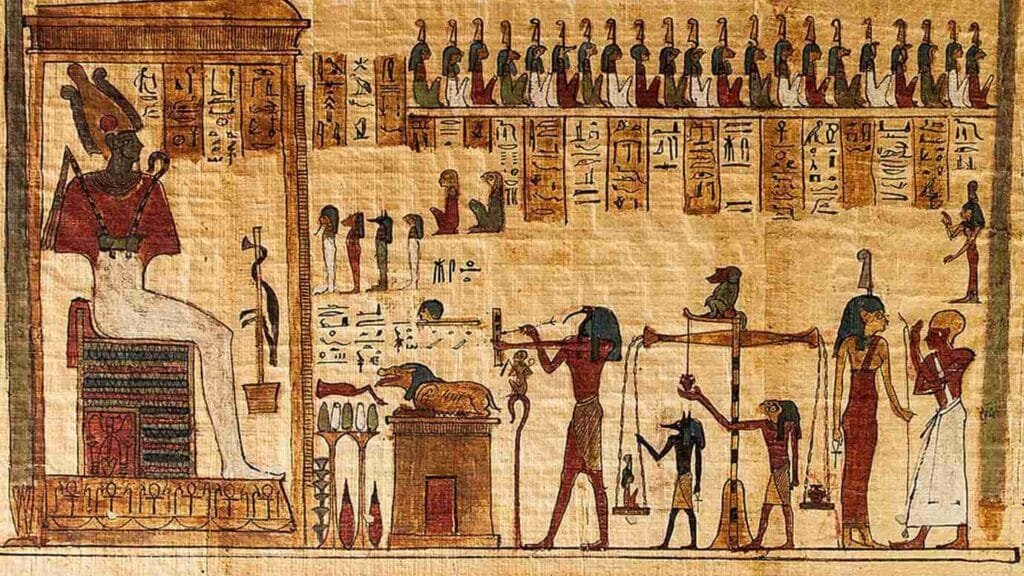
26 . Funeral Rituals in Ancient Egypt
In Ancient Egypt, death was seen as a transition to another realm, and the journey to the afterlife was as important, if not more so, than life itself. Egyptians believed that the soul’s eternal existence depended heavily on the rituals performed after death. These funeral rituals were not only practical but deeply religious,...
27 . Secrets of the Pyramids
The Egyptian pyramids are among the most famous and enigmatic monuments in the world. These massive structures are not only architectural marvels but also hold mysteries about the history of ancient Egypt and its extraordinary civilization. The construction of the pyramids has fascinated people for centuries,...
28 . The Wonders of Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt, one of the earliest and most advanced civilizations, made significant contributions to science and technology. Their achievements in various fields such as medicine, engineering, mathematics, astronomy, and agriculture were far ahead of their time. The Egyptians were not only ...
29 . Top 10 Must-Visit Sites in Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt is home to a vast array of monuments, temples, and tombs, each telling a unique story about the civilization that flourished along the Nile for thousands of years. Whether you’re an avid history enthusiast or simply captivated by ancient cultures, Egypt has no shortage of sites to explore. Below are the top 10 must-visit sites in Ancient Egypt ...
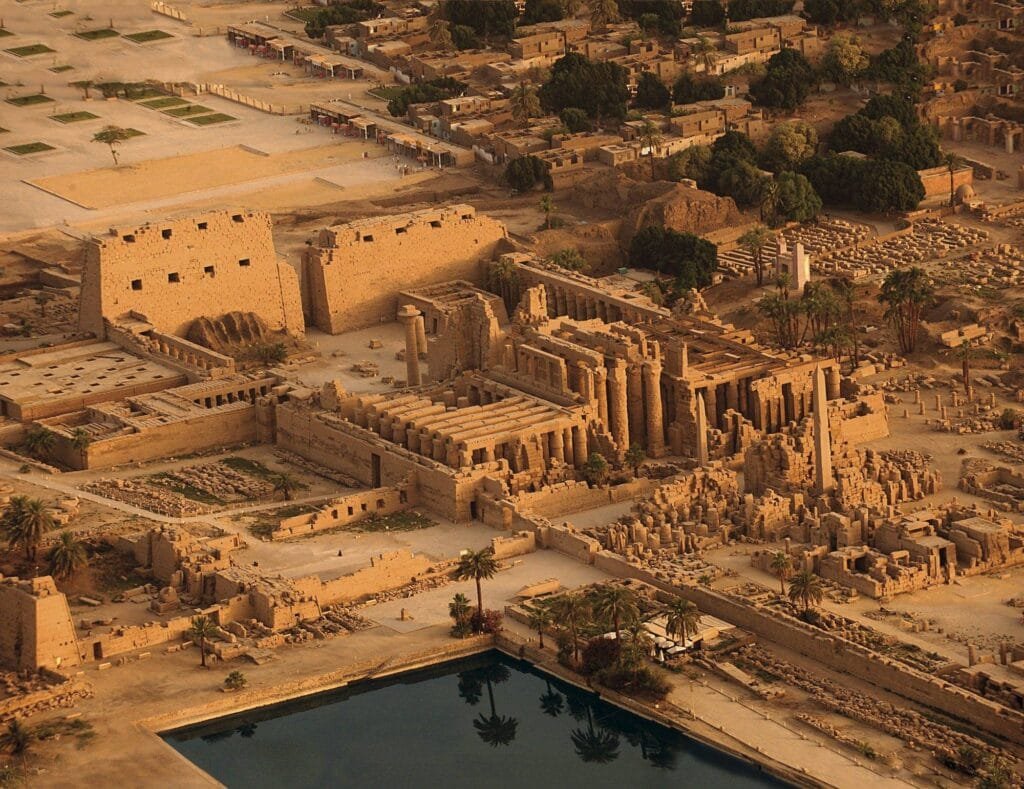
30. The Temples of Karnak , A Walk Through Ancient Egypt’s Spiritual Heart
Nestled in the heart of Luxor, the Karnak Temple Complex stands as a monumental testament to the grandeur and spiritual depth of ancient Egypt. Serving as a vital religious site for over 2,000 years, Karnak is one of the most impressive archaeological wonders in Egypt, drawing visitors from all over the world who are eage ...
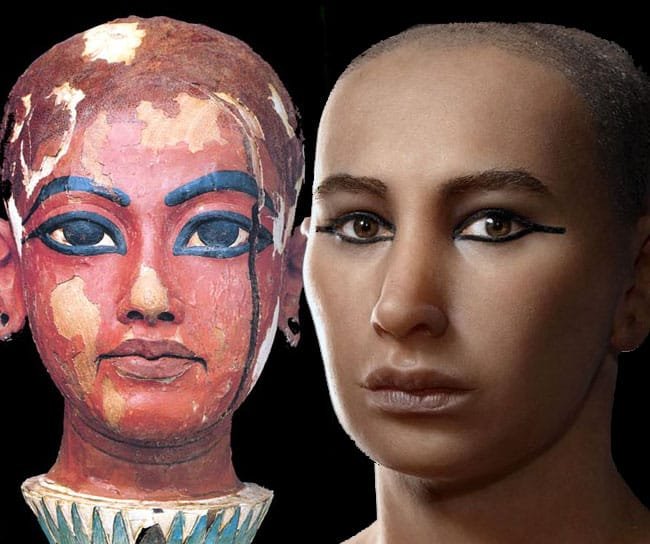
31 . The Story of King Tut , The Boy Pharaoh
King Tutankhamun, the famed Boy Pharaoh of ancient Egypt, is a figure whose life and death continue to intrigue historians and archaeologists alike. Despite his short reign, lasting only ten years, Tut’s story is woven with mystery, as much of what we know about him comes from the discovery of his nearly intact tomb in 1922. The treasures found within the tomb and ...
32 . Exploring the Pyramids , Mysteries of the Great Pyramid of Giza
The Great Pyramid of Giza stands as one of the most iconic and enduring symbols of ancient Egypt, attracting millions of visitors and scholars from around the world. Built over 4,500 years ago during the reign of Pharaoh Khufu, this awe-inspiring monument continues to captivate the imagination, .
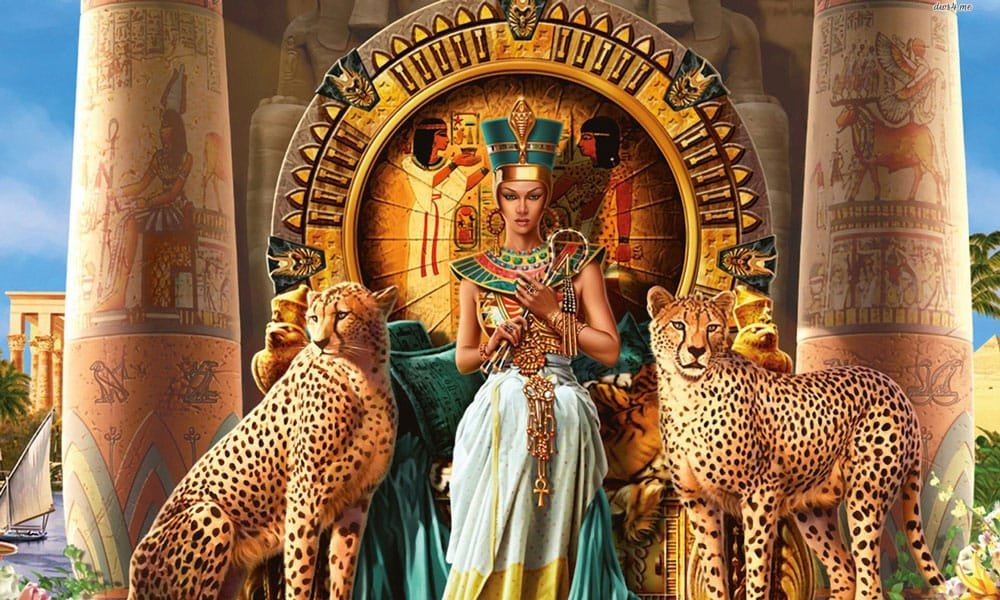
33 . Cleopatra , The Last Pharaoh of Egypt
Cleopatra VII, the last active ruler of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt, is one of the most famous figures in ancient history. Her legacy as a powerful queen, political strategist, and lover of two of the most influential Roman leaders—Julius Caesar and Mark Antony—has fascinated historians and tourists alike for centuries. Cleopatra’s reign marked the end of an era for Egypt ...
34 . Valley of the Kings , Tombs of Ancient Egypt
The Valley of the Kings, located on the west bank of the Nile River near Luxor, is one of Egypt’s most significant and awe-inspiring archaeological sites. This ancient burial ground was the final resting place for many of Egypt’s most famous Pharaohs, queens, and elites, including Tutankhamun, Ramses the Great, and Seti I....
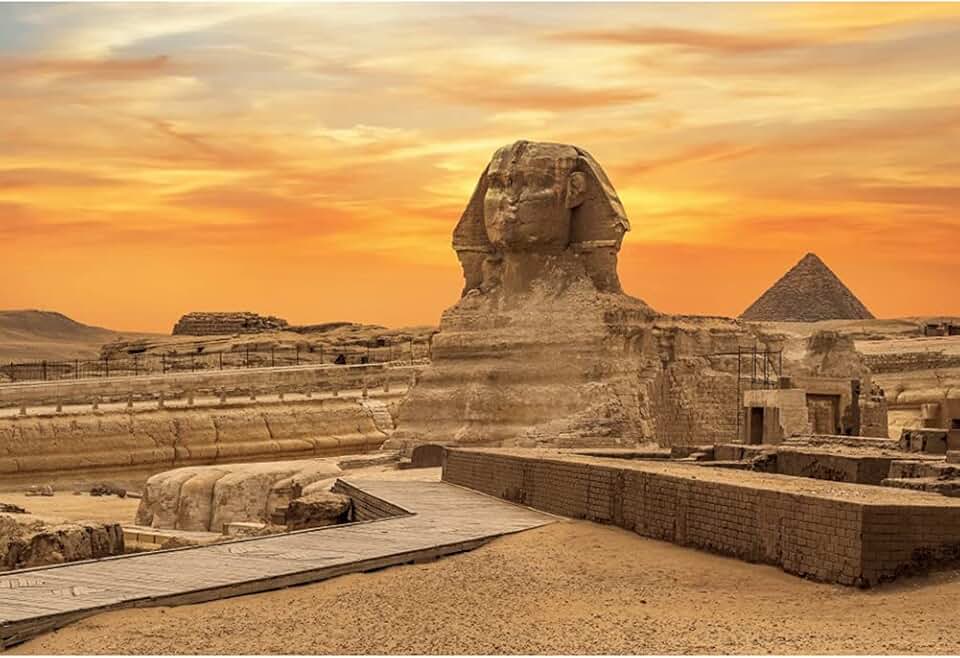
35 . The Sphinx , Guardian of the Giza Plateau
The Great Sphinx of Giza, an iconic symbol of Ancient Egypt, stands as one of the world’s most famous and mysterious monuments. Located on the Giza Plateau, the Sphinx is a monumental limestone statue with the body of a lion and the head of a Pharaoh, traditionally believed to represent Pharaoh Khafre. ...
36 . Pharaohs and Their Gods
Ancient Egypt is a land filled with awe-inspiring monuments, colossal temples, and intricate hieroglyphics that speak volumes about the civilization’s religious beliefs. The religion of the ancient Egyptians was deeply intertwined with their daily life, culture, and governance, with the Pharaohs serving as the divine link between the gods and the people. For those visiting Egypt ...
37 . Daily life in Ancient Egypt
Imagine waking up thousands of years ago in the heart of ancient Egypt—surrounded by the vast desert, the mighty Nile River, and the towering monuments that have stood the test of time. What would it have been like to live in one of the most fascinating and influential civilizations in history? From the moment the sun rises to the time it sets over the river,