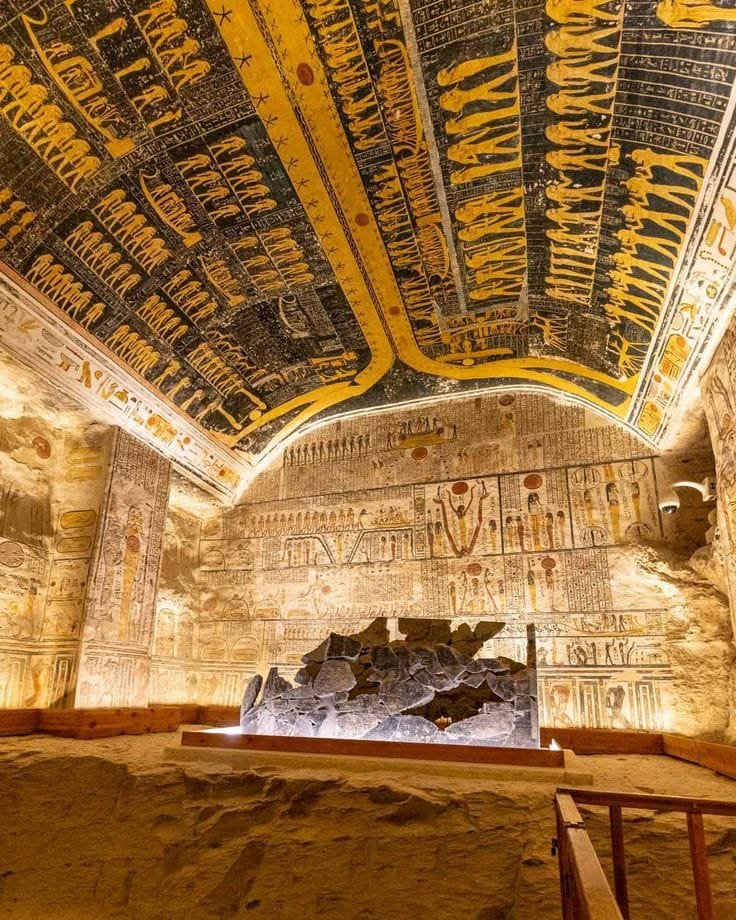
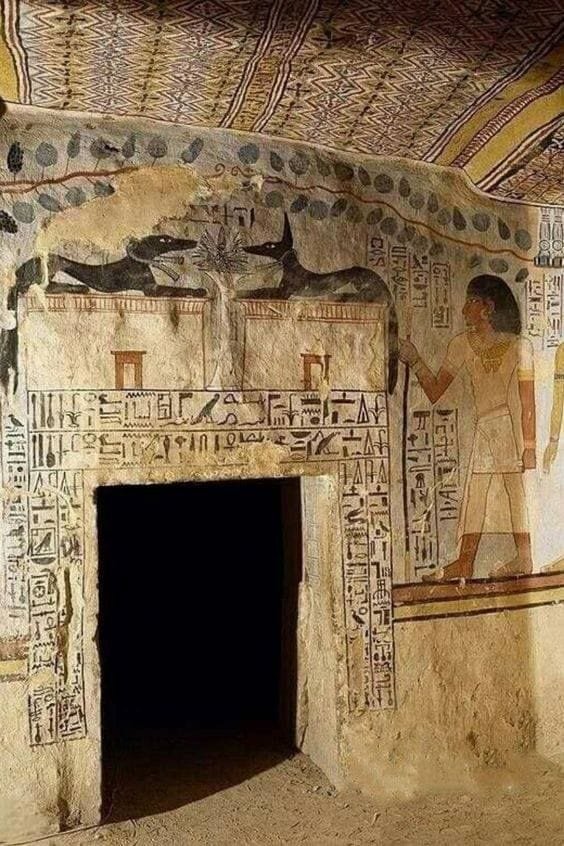
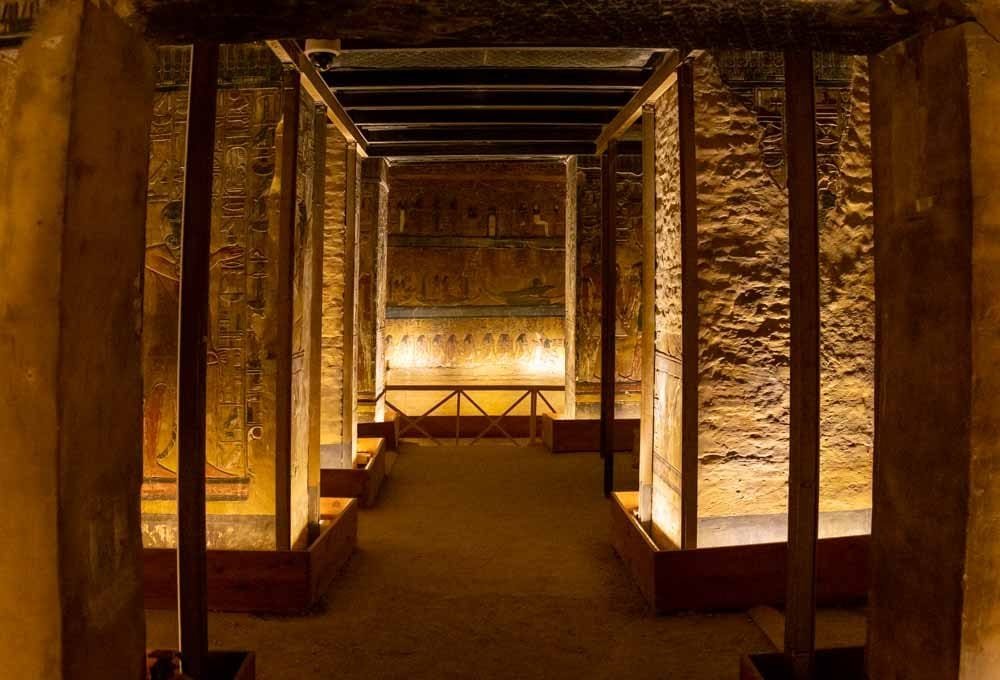
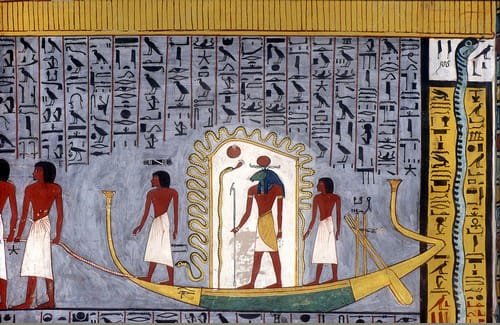
The Tomb of King Seti I (KV16) is one of the most remarkable and extensively decorated tombs in the Valley of the Kings. Seti I, the second pharaoh of the 19th Dynasty, reigned from 1290 to 1279 BC and is often regarded as one of ancient Egypt’s greatest military leaders and builders. His tomb, located in the heart of the Valley of the Kings, reflects his greatness and the impressive artistry of his reign. Although it was originally constructed to serve as Seti’s final resting place, the tomb also provides valuable insight into the religious and funerary practices of the New Kingdom.
Egypt Tour Magic
Each tour type can be adjusted in terms of duration, activities, and accommodations to best meet the needs and interests of your clients.
About Us
Embark on a journey with Egypt Tour Magic and discover the magic of Egypt like never before …
Our Services
Discover the magic of Egypt with Egypt Tour Magic, where every detail is taken care of to ensure..
Our Team
At Egypt Tour Magic, our dedicated team is passionate about creating unforgettable travel experiences....
Refund and Returns Policy
At Egypt Tour Magic, we strive to provide exceptional travel experiences. However ..
Contact Us
We’re here to help you with any questions or to assist you in planning your next ..
Egypt Tour Magic
Explore More About Us