Ancient Egypt, a civilization known for its monumental achievements and rich culture, also had a well-developed system of law and order. Much like the modern police forces of today, the ancient Egyptian police played a crucial role in maintaining stability and ensuring that the laws set forth by the pharaohs were followed. These early law enforcers were involved in various aspects of society, from protecting sacred sites to investigating crimes and upholding public order. Let’s delve into the different aspects of the ancient Egyptian police force and the key roles they played.
- Egypt Tour Magic
- Egypt Tour Packages
- Excursions in Egypt
- Cairo Tours and Excursions
- Hurghada Tours and Excursions
- Soma Bay Tours and Excursions
- Makadi Bay Tours and Excursions
- Sahl Hasheesh Tours and Excursions
- El Gouna Tours and Excursions
- Marsa Alam Tours and Excursions
- Port Ghalib Tours and Excursions
- El Quseir Tours and Excursions
- Dendera and Abydos Day Tours
- Aswan Tours and Excursions
- Luxor Tours and Excursions
- Alexandria Tours and Excursions
- Sharm El Sheikh Tours and Excursions
- Top Rated Tours in 2025
- Optional Excursions in Egypt
- Private Transfer
- Blogs About egypt
- Ancient Egypt
- What You Need To know Before Your First Trip To Egypt
- Best Places to Visit in Egypt 2025
- Top Attractions in Red Sea Resorts 2025
- Top 10 Tourist Activities in Egypt
- Top 30 Activities You Can’t Miss in Egypt
- The Guide to Guided Tours in Egypt
- Egypt’s Ancient and Modern History
- The Nile River
- The Deserts of Egypt
- Historical Sites in Egypt
- Cairo
- Alexandria
- Luxor
- Aswan
- The Red Sea
- Dendera Temple
- El Fayoum Oasis
- Bahariya Oasis
- Siwa Oasis
- Al Alamein
- Marsa Matruh
- Ancient Egyptian gods
- famous Egyptian dishes
- UNESCO World Heritage sites
- About Us
- Why Egypt Tour Magic
- Egypt Tour Magic
- Egypt Tour Packages
- Excursions in Egypt
- Cairo Tours and Excursions
- Hurghada Tours and Excursions
- Soma Bay Tours and Excursions
- Makadi Bay Tours and Excursions
- Sahl Hasheesh Tours and Excursions
- El Gouna Tours and Excursions
- Marsa Alam Tours and Excursions
- Port Ghalib Tours and Excursions
- El Quseir Tours and Excursions
- Dendera and Abydos Day Tours
- Aswan Tours and Excursions
- Luxor Tours and Excursions
- Alexandria Tours and Excursions
- Sharm El Sheikh Tours and Excursions
- Top Rated Tours in 2025
- Optional Excursions in Egypt
- Private Transfer
- Blogs About egypt
- Ancient Egypt
- What You Need To know Before Your First Trip To Egypt
- Best Places to Visit in Egypt 2025
- Top Attractions in Red Sea Resorts 2025
- Top 10 Tourist Activities in Egypt
- Top 30 Activities You Can’t Miss in Egypt
- The Guide to Guided Tours in Egypt
- Egypt’s Ancient and Modern History
- The Nile River
- The Deserts of Egypt
- Historical Sites in Egypt
- Cairo
- Alexandria
- Luxor
- Aswan
- The Red Sea
- Dendera Temple
- El Fayoum Oasis
- Bahariya Oasis
- Siwa Oasis
- Al Alamein
- Marsa Matruh
- Ancient Egyptian gods
- famous Egyptian dishes
- UNESCO World Heritage sites
- About Us
- Why Egypt Tour Magic
The Police in Ancient Egypt: Guardians of Order and Justice
The Role of Law Enforcement in Ancient Egypt
Law and order in ancient Egypt were deeply rooted in the concept of Maat—a divine principle representing truth, justice, balance, and cosmic order. The ancient Egyptians believed that maintaining Maat was essential for the prosperity of the land and the well-being of its people. The pharaoh, as both the political and divine ruler, was the protector of Maat. In this context, the role of the police was not just to enforce laws, but also to maintain this sacred balance in society. The police ensured that criminals were held accountable, public spaces remained peaceful, and the people lived according to the laws of the land. Their actions helped maintain the stability and order that was critical to the survival of ancient Egypt.
Structure and Organization of the Police Force
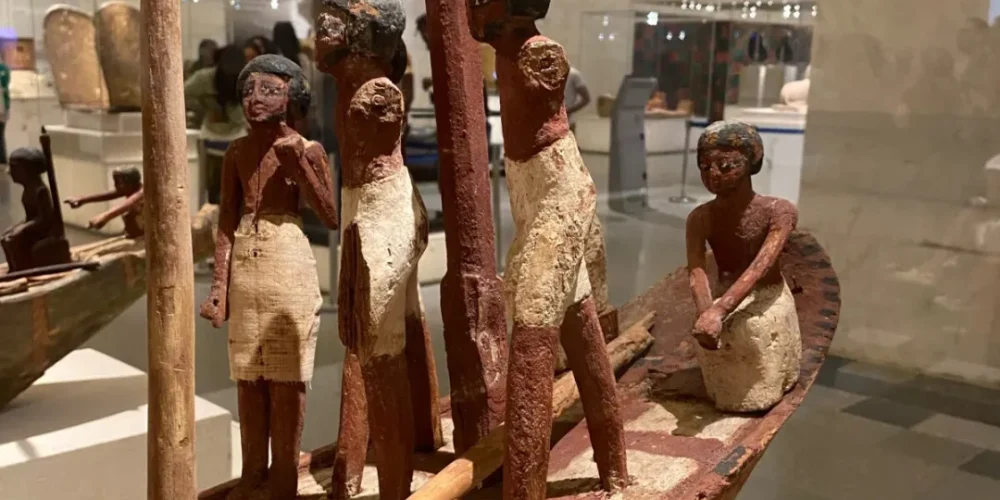
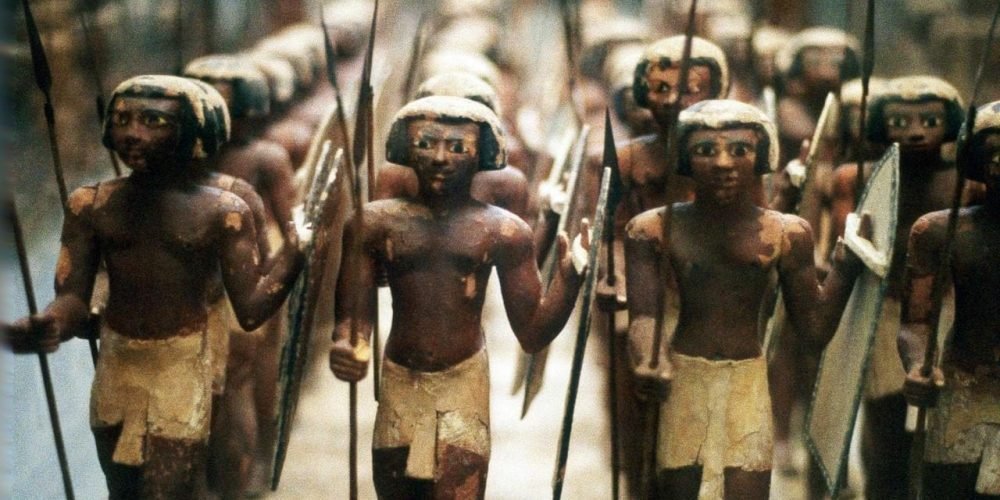
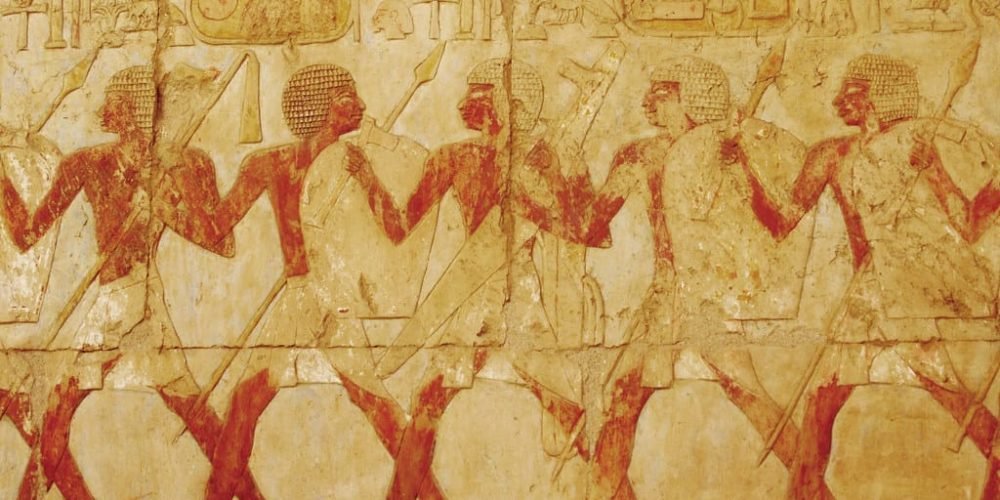
The structure of the police in ancient Egypt was relatively decentralized, with various groups tasked with different duties. Unlike modern centralized police forces, the ancient Egyptian police system was composed of local officials, military personnel, and temple guards who all had overlapping responsibilities in maintaining law and order. One of the most notable police groups was the Medjay, who originally came from Nubia. The Medjay evolved from a group of desert scouts and became elite police officers assigned to protect important locations, such as royal tombs, trade routes, and temples. These officers played a crucial role in safeguarding Egypt’s treasures and ensuring the security of the pharaoh and the people. In addition to the Medjay, other officials and military personnel were often called upon to enforce the law, especially in urban areas or during times of unrest.
The Medjay: Elite Scouts and Protectors
One of the most iconic groups associated with law enforcement in ancient Egypt was the Medjay. Initially, the Medjay were a nomadic tribe from Nubia, but over time they were recruited into Egypt’s military and law enforcement system. They became well-known as elite scouts and police officers, providing protection in various areas such as the desert, royal palaces, and trade routes. Their primary role was to protect the country from external threats and to ensure the safe passage of goods and people along Egypt’s trade routes. As time passed, the Medjay also became involved in domestic law enforcement, overseeing the markets, investigating crimes, and enforcing the pharaoh’s laws. Their reputation as fierce and skilled warriors made them an ideal force to serve as protectors of Egypt’s borders, sacred sites, and royal properties.
Temple Guards: Protectors of the Sacred
In ancient Egypt, temples were not only places of worship but also housed the divine statues and treasures that were central to religious life. Protecting these sacred spaces was crucial, and this duty fell to a specialized group of police officers known as temple guards. These guards were responsible for ensuring that the temples remained undisturbed by thieves or vandals. They were often highly trained, not just in security measures but also in understanding the religious importance of the temple. The guards’ role went beyond security; they were also tasked with protecting the priests and assisting in religious ceremonies. They kept watch over the treasures, sacred scrolls, and divine relics, ensuring that these invaluable items were safe from theft and desecration.
The Pharaoh’s Guard: Ultimate Protection
The highest level of law enforcement in ancient Egypt was provided by the pharaoh’s personal guard. The pharaoh, as the living god and ruler of Egypt, required the utmost protection, and this was provided by an elite group of guards. These officers were highly trained in combat and espionage and were responsible for the safety of the pharaoh at all times. The pharaoh’s guards were stationed near the royal palace, and their duties included both protection from assassination and maintaining order during royal events and ceremonies. Given the importance of the pharaoh’s safety, these guards were often tasked with investigating potential threats, whether internal conspiracies or external dangers. Their training and loyalty were vital in ensuring the pharaoh’s continued reign and the stability of the Egyptian state.
The Police’s Role in Crime and Punishment
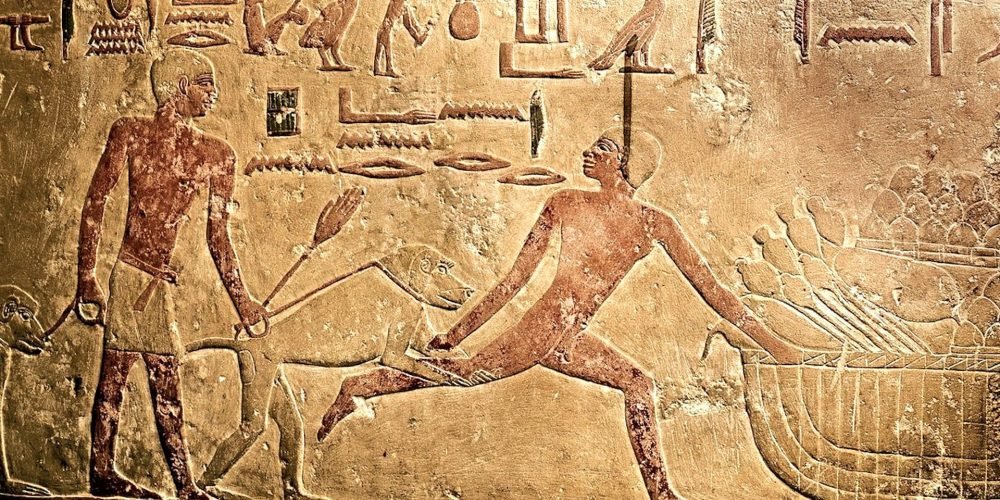
The police in ancient Egypt were not only responsible for maintaining public order but also for investigating crimes and administering justice. When a crime was committed, it was the police’s duty to investigate, gather evidence, and bring the criminal to justice. Ancient Egyptians used various methods of criminal investigation, including gathering witness testimonies and searching for physical evidence. Once a suspect was identified, the police worked with scribes to document the case, creating official records. Punishments for crimes ranged from fines and corporal punishment for minor offenses to execution for more severe crimes, such as murder or treason. The severity of the punishment often depended on the nature of the crime and the social status of the perpetrator. The police were instrumental in enforcing the laws set by the pharaoh, ensuring that order was maintained and justice was served.
Maintaining Public Order and Safeguarding Trade
In addition to dealing with serious crimes, the police in ancient Egypt also had the important task of maintaining public order in the streets and marketplaces. As Egypt’s cities and trade networks grew, it became increasingly important to regulate activities and ensure that people obeyed public codes of behavior. Police officers were often stationed in markets, overseeing transactions and ensuring that business was conducted fairly. They were also tasked with preventing theft, enforcing taxes, and ensuring that goods were weighed accurately. During large public events, such as festivals or religious processions, the police played a role in crowd control and preventing disturbances. In this way, they helped maintain the day-to-day functioning of society, ensuring the smooth operation of both the economy and public life.
The Legacy of Law Enforcement in Ancient Egypt
The role of the police in ancient Egypt was far-reaching, deeply integrated into the political, social, and religious fabric of the civilization. From protecting sacred temples to investigating crimes and ensuring order in public spaces, the police served as the enforcers of the pharaoh’s laws and the guardians of Egypt’s stability. Their contributions to maintaining Maat, or divine justice, helped ensure the longevity of one of the world’s greatest civilizations. The legacy of the ancient Egyptian police can be seen in the modern systems of law enforcement, where the fundamental principles of protecting society, investigating crimes, and ensuring fairness still hold true today. Ancient Egypt’s police force was not just about enforcing the law—it was about maintaining balance, protecting the divine, and safeguarding the prosperity of the state.