The Nile River is one of the most important and iconic rivers in the world, known for its immense contribution to the rise of ancient Egypt and its ongoing influence on the country. Spanning approximately 6,650 kilometers, the Nile is the longest river on Earth and flows through 11 countries in northeastern Africa. For thousands of years, the Nile has been the lifeblood of Egypt, providing water, sustenance, and a means of transport. Here are six key points about the Nile River and its enduring importance to Egypt.
- Egypt Tour Magic
- Egypt Tour Packages
- Excursions in Egypt
- Cairo Tours and Excursions
- Hurghada Tours and Excursions
- Soma Bay Tours and Excursions
- Makadi Bay Tours and Excursions
- Sahl Hasheesh Tours and Excursions
- El Gouna Tours and Excursions
- Marsa Alam Tours and Excursions
- Port Ghalib Tours and Excursions
- El Quseir Tours and Excursions
- Dendera and Abydos Day Tours
- Aswan Tours and Excursions
- Luxor Tours and Excursions
- Alexandria Tours and Excursions
- Sharm El Sheikh Tours and Excursions
- Top Rated Tours in 2025
- Optional Excursions in Egypt
- Private Transfer
- Blogs About egypt
- Ancient Egypt
- What You Need To know Before Your First Trip To Egypt
- Best Places to Visit in Egypt 2025
- Top Attractions in Red Sea Resorts 2025
- Top 10 Tourist Activities in Egypt
- Top 30 Activities You Can’t Miss in Egypt
- The Guide to Guided Tours in Egypt
- Egypt’s Ancient and Modern History
- The Nile River
- The Deserts of Egypt
- Historical Sites in Egypt
- Cairo
- Alexandria
- Luxor
- Aswan
- The Red Sea
- Dendera Temple
- El Fayoum Oasis
- Bahariya Oasis
- Siwa Oasis
- Al Alamein
- Marsa Matruh
- Ancient Egyptian gods
- famous Egyptian dishes
- UNESCO World Heritage sites
- About Us
- Why Egypt Tour Magic
- Egypt Tour Magic
- Egypt Tour Packages
- Excursions in Egypt
- Cairo Tours and Excursions
- Hurghada Tours and Excursions
- Soma Bay Tours and Excursions
- Makadi Bay Tours and Excursions
- Sahl Hasheesh Tours and Excursions
- El Gouna Tours and Excursions
- Marsa Alam Tours and Excursions
- Port Ghalib Tours and Excursions
- El Quseir Tours and Excursions
- Dendera and Abydos Day Tours
- Aswan Tours and Excursions
- Luxor Tours and Excursions
- Alexandria Tours and Excursions
- Sharm El Sheikh Tours and Excursions
- Top Rated Tours in 2025
- Optional Excursions in Egypt
- Private Transfer
- Blogs About egypt
- Ancient Egypt
- What You Need To know Before Your First Trip To Egypt
- Best Places to Visit in Egypt 2025
- Top Attractions in Red Sea Resorts 2025
- Top 10 Tourist Activities in Egypt
- Top 30 Activities You Can’t Miss in Egypt
- The Guide to Guided Tours in Egypt
- Egypt’s Ancient and Modern History
- The Nile River
- The Deserts of Egypt
- Historical Sites in Egypt
- Cairo
- Alexandria
- Luxor
- Aswan
- The Red Sea
- Dendera Temple
- El Fayoum Oasis
- Bahariya Oasis
- Siwa Oasis
- Al Alamein
- Marsa Matruh
- Ancient Egyptian gods
- famous Egyptian dishes
- UNESCO World Heritage sites
- About Us
- Why Egypt Tour Magic
The Nile River: Egypt’s Lifeblood

1. The Role of the Nile in Ancient Egypt
The Nile was the cornerstone of ancient Egyptian civilization. Ancient Egyptians often referred to the Nile as the "gift of the gods," as it provided the essential resources needed to support one of the world’s greatest ancient civilizations. The Nile’s annual flooding, or Inundation, transformed the surrounding desert into fertile land, allowing Egyptians to grow crops in an otherwise arid environment. This regular flooding deposited nutrient-rich silt onto the soil, making agriculture possible. Crops such as wheat, barley, and flax flourished along the river’s banks, which provided not only sustenance but also materials for clothing and papyrus, vital for writing and communication. The fertility of the Nile’s valley became the backbone of Egypt’s economy, ensuring a steady food supply for the growing population. With this surplus, Egypt was able to develop sophisticated infrastructure, including monumental architecture like the pyramids, temples, and tombs that still stand today. Agriculture also facilitated the growth of Egypt’s population, which allowed the civilization to thrive for thousands of years. The Nile also played an essential role in transportation and trade. Egyptians built boats and ships to navigate its waters, transporting goods like grain, gold, and luxury items. The river served as a natural highway, connecting Upper and Lower Egypt, and enabled Egyptians to engage in trade with neighboring regions such as Nubia and the Mediterranean coast. This established Egypt as a hub of trade and cultural exchange.
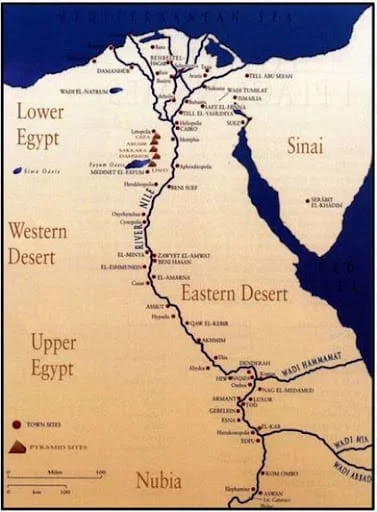
2. The Unique Geography of the Nile
The geography of the Nile River is as fascinating as its historical significance. Unlike most rivers, the Nile flows from south to north, beginning in the highlands of East Africa and traveling through eleven countries before emptying into the Mediterranean Sea. This northward direction of flow is a defining characteristic of the river, and it plays a key role in the agricultural productivity of Egypt. It brings water from the tropical regions of East Africa, where rainfall is more abundant, and deposits it into Egypt’s largely desert landscape, transforming the surrounding land into fertile farmland. The Nile is made up of two major branches: the White Nile and the Blue Nile. The White Nile, originating from Lake Victoria in Uganda, is the longer of the two and flows through Sudan, eventually joining the Blue Nile in Khartoum, Sudan. The Blue Nile begins at Lake Tana in Ethiopia and contributes the majority of the water and sediment to the river. When these two rivers converge, they create the mighty Nile, which winds through Egypt, providing life and sustenance to the land. Along its journey through Egypt, the Nile creates a narrow strip of fertile land known as the Nile Valley. The valley is flanked by vast deserts on both sides, and it is this small, green ribbon of land that has sustained Egypt’s population for millennia. The majority of Egypt’s population lives along this fertile strip, and the river serves as the backbone of Egypt’s economy, agriculture, and daily life.
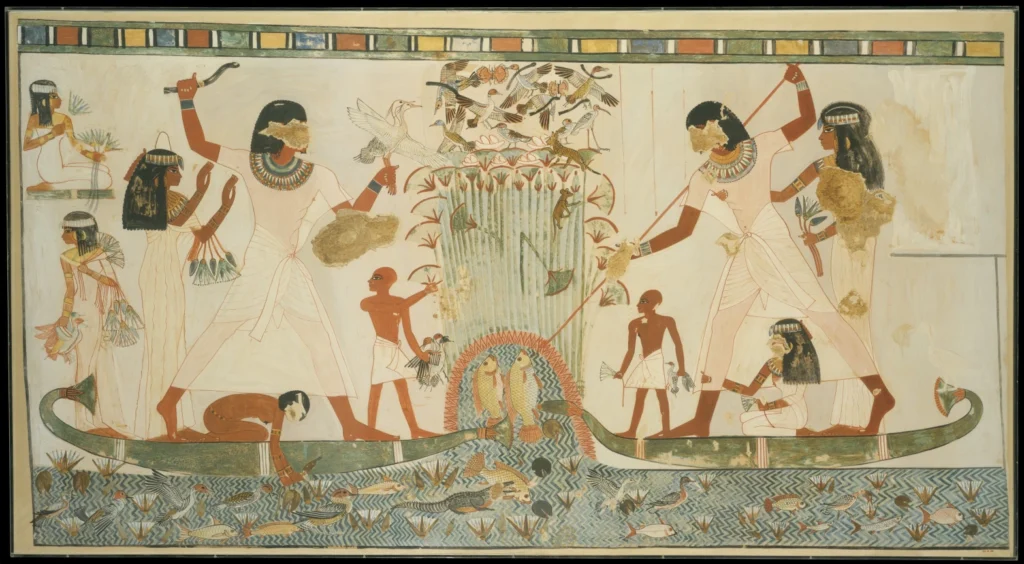

3. The Nile’s Influence on Ancient Egyptian Culture
The Nile River profoundly influenced not only the physical life of ancient Egyptians but also their cultural and spiritual beliefs. In ancient Egyptian religion, the river was seen as a divine entity, personified by the god Hapi, who was believed to control the annual flooding of the river and bring fertility to the land. The Nile’s predictable flooding, which occurred around the same time each year, was viewed as a sign of the gods' favor, ensuring bountiful harvests and the continuity of Egyptian civilization. The Egyptians viewed the Nile as a bridge between life and the afterlife. It was believed that the souls of the deceased traveled along the river to reach the afterlife, a journey symbolizing death and rebirth. Many tombs and monuments, including the famous pyramids, were built along the river’s banks, aligning with the belief that the Nile was a conduit to the divine. The pyramids of Giza, located near the river, are one of the most prominent symbols of Egypt’s connection to the Nile and its eternal legacy. The Nile also played a critical role in Egypt’s art, culture, and language. The river’s significance can be seen in Egyptian hieroglyphs, where depictions of the Nile and its life-giving properties were featured in many texts. Egyptian artists often painted scenes of the river, crops, and agricultural life, showcasing the central role the Nile played in sustaining their civilization. Its importance in Egyptian culture and religion cannot be overstated, as it was central to their understanding of life, death, and renewal.

4. The Aswan High Dam: A Modern Marvel
In modern times, the Nile’s role in Egypt has changed somewhat, particularly with the construction of the Aswan High Dam in the 1960s. The dam, one of the most ambitious engineering projects in the world, was built to regulate the river’s flow, prevent flooding, and provide a reliable source of water for irrigation. The Aswan High Dam controls the Nile’s annual flooding, which had been unpredictable and sometimes destructive in the past. By managing the flow of water, the dam has made it possible for Egypt to harness the river’s power more effectively, ensuring stable water resources for its growing population. The dam created Lake Nasser, one of the world’s largest artificial lakes, which serves as a massive reservoir to store water for irrigation and electricity generation. The dam also produces hydroelectric power, supplying much-needed energy to Egypt. It provides a consistent and reliable water source for agriculture, allowing Egypt to expand its farming areas, increase crop yields, and support its economy. However, the construction of the dam has not been without controversy. While it has provided Egypt with stability in terms of water supply, it has also caused environmental issues, such as the reduction in the natural flow of sediment that once replenished the soil along the Nile’s banks. This has led to the need for artificial fertilizers, which can be harmful to the environment. The dam has also led to the displacement of local communities, especially in the Nubian region, which was submerged by the creation of Lake Nasser. Despite these challenges, the Aswan High Dam remains an essential part of Egypt’s infrastructure.

5. Challenges Facing the Nile: Water Scarcity and Politics
Despite its long-standing significance, the Nile faces a number of challenges in the modern era. The most pressing issue is water scarcity. Egypt, with a population of over 100 million people, relies almost entirely on the Nile for its freshwater needs. As the population grows and demands for water increase, Egypt faces the challenge of ensuring a sustainable water supply for agriculture, industry, and domestic consumption. This has become particularly critical with climate change, which has altered rainfall patterns in the Nile’s upstream regions, causing unpredictable shifts in the river’s water levels. Another significant challenge facing the Nile is the ongoing political tensions between Egypt and the countries that share the river. The Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD), currently under construction in Ethiopia, has been a point of contention between Egypt, Ethiopia, and Sudan. Ethiopia plans to use the GERD to generate hydroelectric power and regulate the flow of the Blue Nile, which is a major tributary to the Nile. Egypt, which relies on the Nile for 90% of its water, has expressed concerns that the dam could reduce the river’s flow, threatening its water supply and agricultural output. Tensions over the Nile’s water rights have led to negotiations between the three countries, with the goal of reaching an agreement that ensures fair and equitable access to the river's resources. As water scarcity becomes an increasingly urgent issue, the Nile’s future will depend on diplomatic solutions and sustainable management practices among the nations that depend on it.
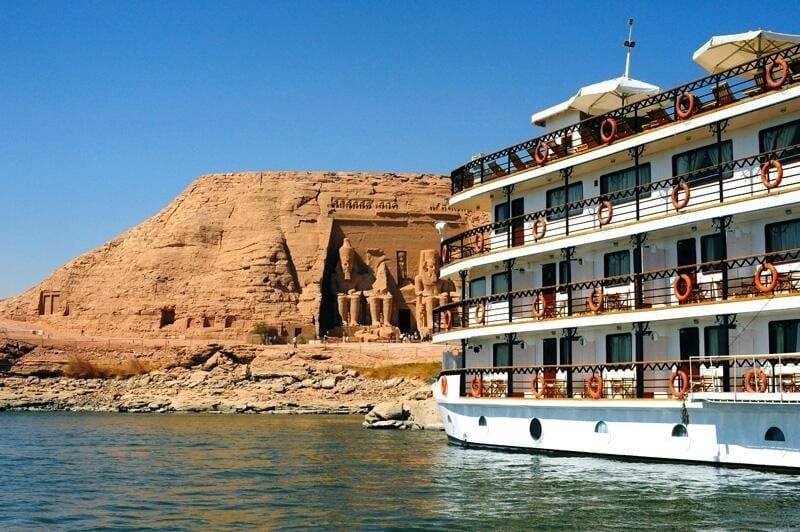

6. Tourism Along the Nile: A Window into Ancient Egypt
Tourism is another vital aspect of the Nile’s importance to Egypt. The river not only sustains life but also draws millions of visitors every year who come to explore Egypt’s ancient wonders. Nile cruises, particularly those between Luxor and Aswan, offer some of the most scenic and culturally rich experiences in the world. As travelers glide along the river’s tranquil waters, they pass by some of Egypt’s most famous archaeological sites, including the Valley of the Kings, the Temple of Karnak, and the Abu Simbel Temples. The Nile also offers visitors the opportunity to explore the vibrant life along its banks, from bustling markets to rural villages where the traditions of ancient Egypt are still alive. As a living river, it continues to support local communities, providing water, transportation, and a sense of continuity. Tourism along the Nile is an important part of Egypt's economy, offering both cultural enrichment and economic benefits. In addition to historical and cultural attractions, the Nile’s natural beauty is a major draw. The river winds through dramatic desert landscapes, and its lush, green banks contrast sharply with the surrounding barren desert. The serene beauty of the river, along with the rich historical context, makes a Nile cruise one of the most memorable travel experiences in the world.


