Ethnic and Religious Composition
Egypt is a homogeneous country with most of its population being of Arab descent. The majority of Egyptians are Sunni Muslims, accounting for about 90% of the population. There is also a significant Christian minority, primarily belonging to the Coptic Orthodox Church, which makes up around 10% of the population. Other Christian denominations, as well as small Jewish and other religious communities, exist but are fewer in number.
Population Distribution
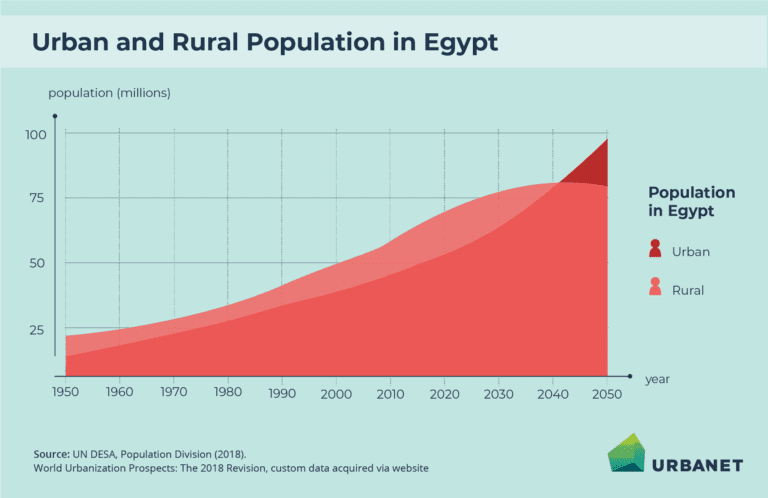
Egypt’s population is concentrated around the Nile River and its delta, which provides fertile land for agriculture and has been the cradle of Egyptian civilization for thousands of years. Despite the large landmass, about 95% of Egypt’s population lives in only 5% of the country’s land area, primarily along the Nile and the Mediterranean coast. The rest of Egypt consists of vast deserts, such as the Western Desert and Eastern Desert, which are sparsely populated.
Challenges of Population Growth
Rapid population growth in Egypt has posed significant challenges to the country’s infrastructure, resources, and environment:
Housing and Urbanization: Rapid urbanization, especially in Cairo, has led to overcrowded living conditions and pressure on housing and public services. Informal settlements are widespread in cities, leading to issues with sanitation, infrastructure, and healthcare access.
Water Scarcity: With a large population concentrated along the Nile River, Egypt faces challenges related to water scarcity. The country relies heavily on the Nile for its water needs, but it has limited access to other water resources, making the management of this precious resource critical for future development.
Job Creation and Economy: Egypt’s youth bulge presents both opportunities and challenges. While young people represent a potential workforce, the country must create millions of jobs to accommodate this growing demographic. Unemployment, particularly among young graduates, remains a significant issue.
Healthcare and Education: Providing adequate healthcare and education for Egypt’s growing population is an ongoing challenge. The government continues to invest in expanding these sectors, but the growing demand often outpaces the available resources.
Conclusion
Egypt’s population is a reflection of its ancient history, its modern challenges, and its opportunities for the future. With a population of around 110 million people, Egypt faces challenges related to rapid growth, urbanization, and resource management. However, this young, dynamic population also presents significant potential for economic and social development. By focusing on sustainable growth, job creation, education, and infrastructure, Egypt can harness its population to fuel future progress while addressing the challenges that come with a growing and increasingly urbanized society.