Ancient Egypt is one of the most fascinating civilizations in history, renowned for its incredible achievements in art, architecture, medicine, and social organization. At the heart of these achievements were the hardworking individuals who performed a vast array of jobs that helped sustain the society for thousands of years. From monumental pyramid builders to skilled scribes, Ancient Egypt’s labor force was diverse and essential for the civilization’s success. Let’s delve deeper into the many jobs that existed in Ancient Egypt, shedding light on the roles and professions that shaped this ancient society.
- Egypt Tour Magic
- Egypt Tour Packages
- Excursions in Egypt
- Cairo Tours and Excursions
- Hurghada Tours and Excursions
- Soma Bay Tours and Excursions
- Makadi Bay Tours and Excursions
- Sahl Hasheesh Tours and Excursions
- El Gouna Tours and Excursions
- Marsa Alam Tours and Excursions
- Port Ghalib Tours and Excursions
- El Quseir Tours and Excursions
- Dendera and Abydos Day Tours
- Aswan Tours and Excursions
- Luxor Tours and Excursions
- Alexandria Tours and Excursions
- Sharm El Sheikh Tours and Excursions
- Top Rated Tours in 2025
- Optional Excursions in Egypt
- Private Transfer
- Blogs About egypt
- Ancient Egypt
- What You Need To know Before Your First Trip To Egypt
- Best Places to Visit in Egypt 2025
- Top Attractions in Red Sea Resorts 2025
- Top 10 Tourist Activities in Egypt
- Top 30 Activities You Can’t Miss in Egypt
- The Guide to Guided Tours in Egypt
- Egypt’s Ancient and Modern History
- The Nile River
- The Deserts of Egypt
- Historical Sites in Egypt
- Cairo
- Alexandria
- Luxor
- Aswan
- The Red Sea
- Dendera Temple
- El Fayoum Oasis
- Bahariya Oasis
- Siwa Oasis
- Al Alamein
- Marsa Matruh
- Ancient Egyptian gods
- famous Egyptian dishes
- UNESCO World Heritage sites
- About Us
- Why Egypt Tour Magic
- Egypt Tour Magic
- Egypt Tour Packages
- Excursions in Egypt
- Cairo Tours and Excursions
- Hurghada Tours and Excursions
- Soma Bay Tours and Excursions
- Makadi Bay Tours and Excursions
- Sahl Hasheesh Tours and Excursions
- El Gouna Tours and Excursions
- Marsa Alam Tours and Excursions
- Port Ghalib Tours and Excursions
- El Quseir Tours and Excursions
- Dendera and Abydos Day Tours
- Aswan Tours and Excursions
- Luxor Tours and Excursions
- Alexandria Tours and Excursions
- Sharm El Sheikh Tours and Excursions
- Top Rated Tours in 2025
- Optional Excursions in Egypt
- Private Transfer
- Blogs About egypt
- Ancient Egypt
- What You Need To know Before Your First Trip To Egypt
- Best Places to Visit in Egypt 2025
- Top Attractions in Red Sea Resorts 2025
- Top 10 Tourist Activities in Egypt
- Top 30 Activities You Can’t Miss in Egypt
- The Guide to Guided Tours in Egypt
- Egypt’s Ancient and Modern History
- The Nile River
- The Deserts of Egypt
- Historical Sites in Egypt
- Cairo
- Alexandria
- Luxor
- Aswan
- The Red Sea
- Dendera Temple
- El Fayoum Oasis
- Bahariya Oasis
- Siwa Oasis
- Al Alamein
- Marsa Matruh
- Ancient Egyptian gods
- famous Egyptian dishes
- UNESCO World Heritage sites
- About Us
- Why Egypt Tour Magic
Exploring Jobs in Ancient Egypt
1. Farmers
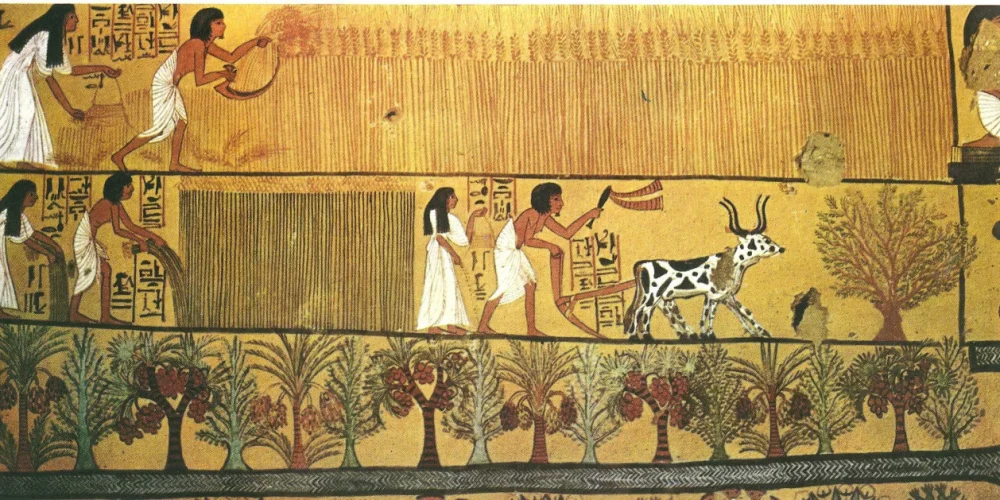
Agriculture was the backbone of Ancient Egypt’s economy, and farmers played a central role in ensuring the survival and prosperity of the civilization. The fertile banks of the Nile River allowed for the cultivation of crops such as wheat, barley, flax, and papyrus, which were vital for food production, trade, and even for creating the materials needed for writing. Farmers grew grains to feed the population and also raised livestock, including cattle, sheep, and goats.
Egypt’s agricultural cycle was directly tied to the annual flooding of the Nile, which deposited rich silt on the land, making it perfect for farming. This made farming a highly seasonal job, with peak periods for planting and harvesting. Farmers would work tirelessly, tending to the land during the planting season, while also maintaining irrigation systems to ensure that crops received enough water throughout the year. It is said that Egyptian farmers were often required to pay taxes in the form of a portion of their crops, a system that ensured the stability of the economy.
2. Craftsmen and Artisans
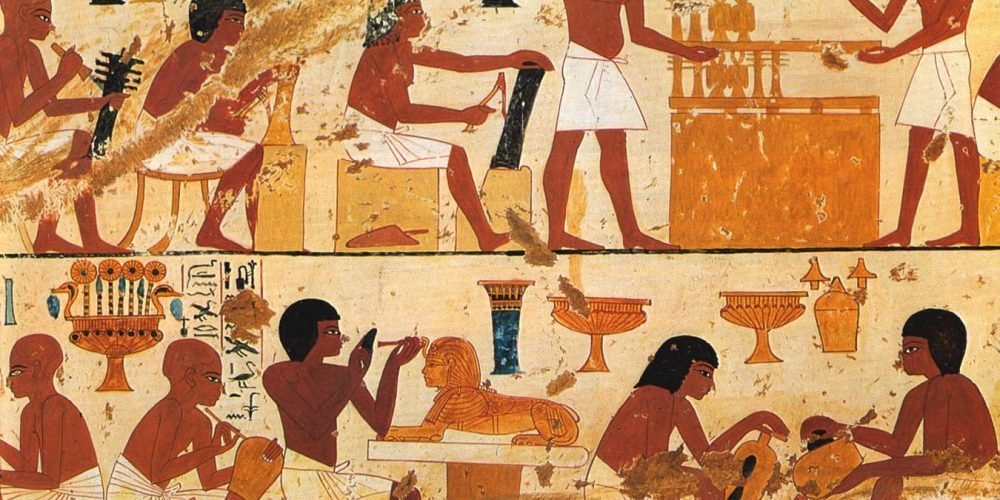
Craftsmen and artisans were crucial to the development of Ancient Egyptian culture and were skilled in many different areas, from pottery and metalwork to jewelry making and sculpture. These workers created the everyday objects used by Egyptian society, as well as the highly prized works of art found in tombs and temples. Artisans were experts in their trades and their products often carried religious or symbolic meanings, making their work an important part of Egyptian rituals.
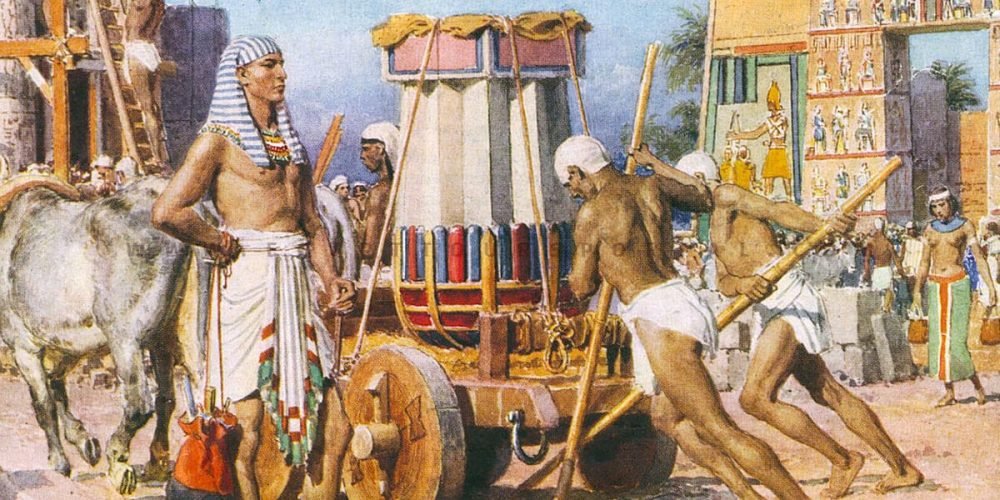
Stone Carvers and Sculptors: One of the most well-known crafts in Ancient Egypt was stone carving. These artisans were responsible for creating the impressive statues, reliefs, and monuments that adorned temples, tombs, and palaces. The Great Sphinx of Giza and the statues of Ramses II at Abu Simbel are prime examples of the incredible work of Egyptian stone carvers.
Jewelry Makers: Ancient Egyptian jewelers were highly skilled in the use of precious metals, semi-precious stones, and glass to create intricate jewelry. Items such as necklaces, bracelets, rings, and amulets were worn by the elite and were often used in burial rituals to ensure a safe passage to the afterlife.
Weavers and Potters: Other artisans produced everyday items like clothing, pottery, and textiles. The Egyptians excelled at weaving linen, which was considered a luxury fabric, and pottery-making, with intricate designs and fine craftsmanship.
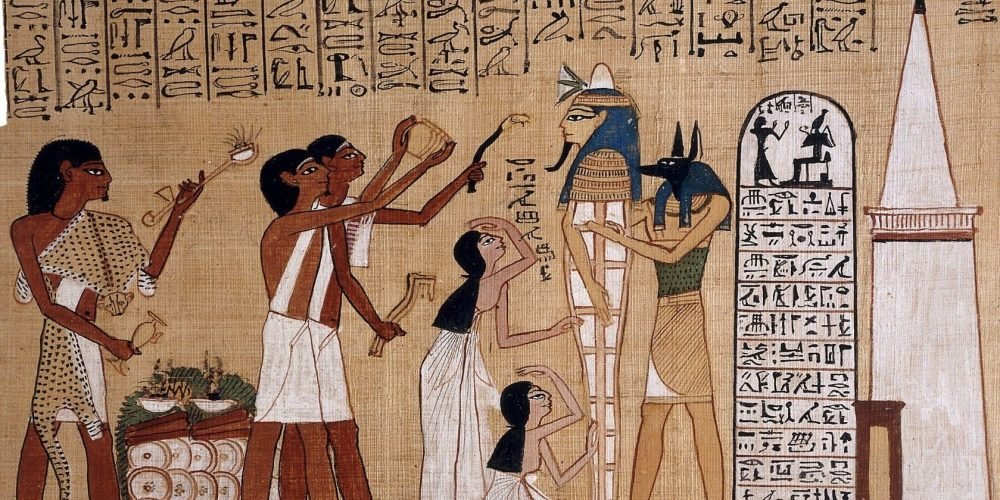
3. Priests and Priestesses
Religion permeated every aspect of Ancient Egyptian life, and the priests and priestesses held an essential role in maintaining the spiritual and divine order. The Egyptians believed that the gods governed every facet of existence, and it was the responsibility of the priesthood to maintain balance by performing religious rituals, offerings, and ceremonies.
Temple Priests: Each major deity in the Egyptian pantheon had a temple where priests and priestesses served. They performed daily rituals and cared for the statues of gods and goddesses. These rituals included prayers, offerings of food and drink, and the lighting of incense to honor the gods.
Divine Advisors: Some priests also held high positions in the royal court, offering guidance to pharaohs and advising them on matters related to governance, the afterlife, and omens. Priests were believed to have the power to communicate with the gods and interpret divine will.
Women in Religion: Priestesses also played a prominent role, especially in temples dedicated to goddesses such as Hathor, Isis, and Sekhmet. These women could hold significant power, particularly in religious and political matters.
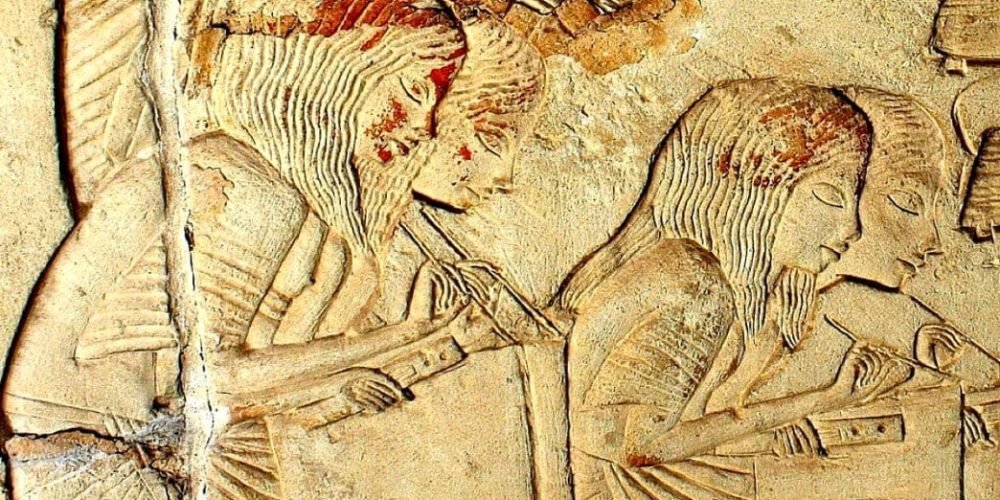
4. Scribes
Scribes were among the most educated individuals in Ancient Egypt. They were responsible for recording and preserving the history, laws, and administrative workings of the kingdom. Scribes had an important role in Egyptian society as they recorded everything from agricultural data to royal decrees, religious texts, and tax records. These written records were vital for the efficient management of Egypt’s vast empire.
Hieroglyphics and Papyrus: Learning to write in hieroglyphics or hieratic script was a long and arduous process. Scribes used these writing systems on materials such as papyrus, ostraca (pottery shards), and leather. The ability to read and write was highly esteemed, and scribes often occupied influential positions within the royal court.
Legal Documents and Taxation: Scribes also handled legal documents, such as contracts and wills, and oversaw the collection of taxes. Their ability to write and interpret texts made them indispensable for administrative duties.
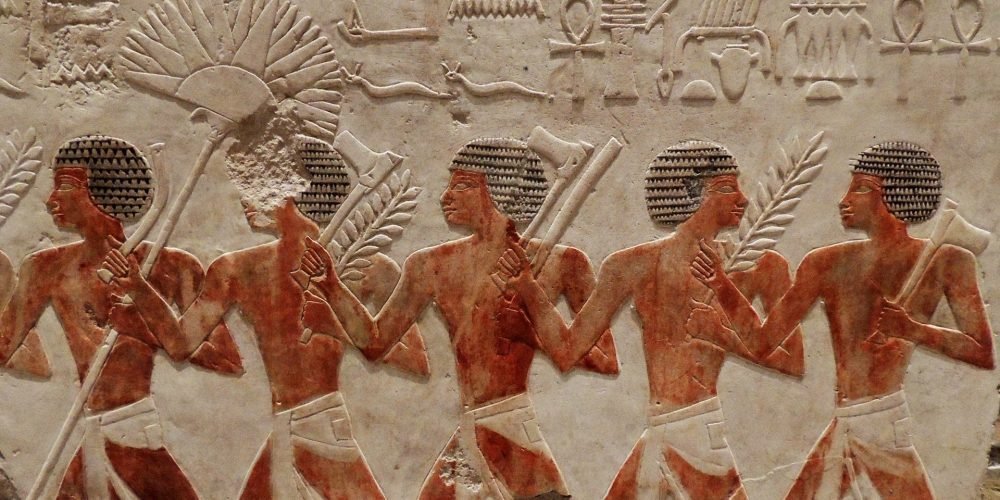
5. Soldiers
The Egyptian military was another vital institution in Ancient Egyptian society, responsible for protecting the kingdom from external threats and maintaining order within its borders. The military also played a significant role in expanding Egypt’s influence through conquest, and many pharaohs gained their status by leading successful military campaigns.
Pharaohs as Military Leaders: Many of the pharaohs, such as Ramses II and Thutmose III, were not only rulers but also skilled military commanders who led their armies into battle. Soldiers were expected to be disciplined and well-trained, and they were often recruited from rural areas during times of conflict.
Specialized Forces: In addition to regular soldiers, Egypt had elite forces, such as chariotry, archers, and the “Medjay,” a group of elite police and military personnel who protected the royal family and maintained law and order throughout Egypt.
6. Merchants and Traders
Merchants and traders helped drive Egypt’s economy by facilitating trade both within the kingdom and with foreign lands. Ancient Egypt was located at the crossroads of Africa and the Middle East, making it a hub for trade routes. Egyptian merchants traded goods such as linen, grain, and papyrus in exchange for luxury items like incense, gold, and exotic animals from far-flung lands.
International Trade Routes: Merchants traveled by land and sea, establishing trade links with regions such as the Levant, Nubia, and the Mediterranean. The trade of valuable resources, including gold and timber, helped Egypt maintain its wealth and power.
Markets and Trading Centers: In cities like Thebes and Memphis, bustling markets attracted traders from across the ancient world. Merchants often dealt in both local goods and foreign commodities, creating a rich exchange of culture and ideas.
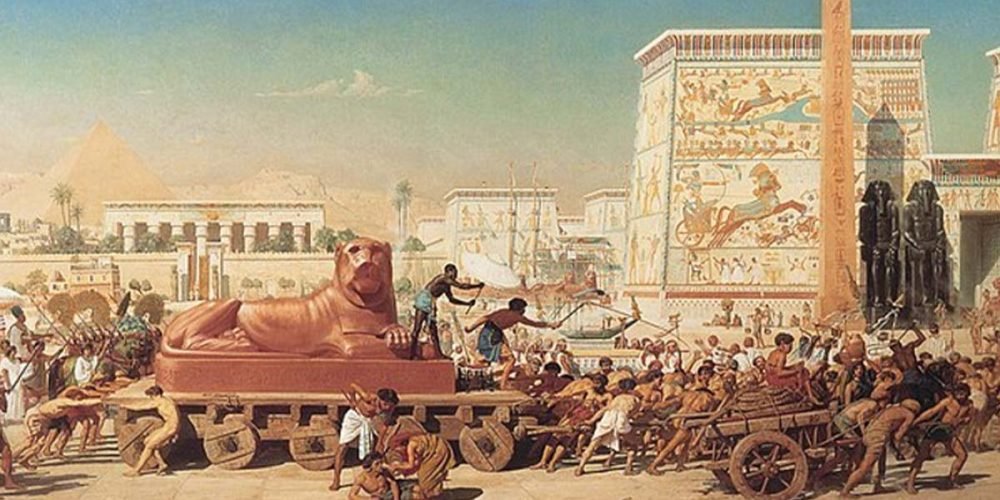
7. Tomb Builders and Mourners
The preparation of tombs for the pharaohs and elite individuals was an essential aspect of ancient Egyptian life, reflecting their beliefs about the afterlife. Tomb builders were tasked with constructing elaborate burial chambers, often adorned with detailed artwork depicting the deceased’s journey to the afterlife. These tombs, including the famous Valley of the Kings, housed the mummies of kings and nobles along with treasures meant to ensure a comfortable afterlife.
Tomb Decorations and Mummification: The craftsmen involved in tomb decoration used vibrant colors and detailed scenes to illustrate the deceased’s journey to the afterlife. Additionally, priests and embalmers played an important role in mummification, ensuring that the body was preserved for the soul’s eternal journey.
Funeral Rituals: Mourners, including family members and professional mourners, would engage in rituals and processions to honor the deceased. These rituals were meant to ensure the safe passage of the deceased into the afterlife.
Conclusion: The Legacy of Ancient Egyptian Workers
The jobs in Ancient Egypt were essential for the functioning of the society and contributed to the civilization’s longevity and greatness. From farmers cultivating crops along the Nile to priests ensuring religious harmony, each profession played a key role in supporting the culture, economy, and power of Egypt. The immense structures, intricate artwork, and rich history left behind by these workers continue to inspire and educate people around the world. The jobs of Ancient Egypt remind us of the diverse and specialized labor forces that contribute to the success of any civilization, creating a lasting legacy that stands the test of time.